Law of Sines or Sine Rule
Related Pages
Law Of Cosines
Lessons On Trigonometry
More Algebra 2 Lessons
These lessons with examples, solutions, and videos to help High School students learn to use the law of sines.
In these lessons, we will learn
- the Law of Sines,
- how to use the Law of Sines when given two angles and one side,
- how to use the Law of Sines when given two sides and a non-included angle,
- about the ambiguous case when using the Law of Sines,
- about the "no solutions" case when using the Law of Sines,
- the proof for the Law of Sines,
- how to solve applications or word problems using the Law of Sines.
Law of Sines
The Law of Sines states that:
In any given triangle, the ratio of the length of a side and
the sine of the angle opposite that side is a constant.
The following figure shows the Law of Sines for the triangle ABC
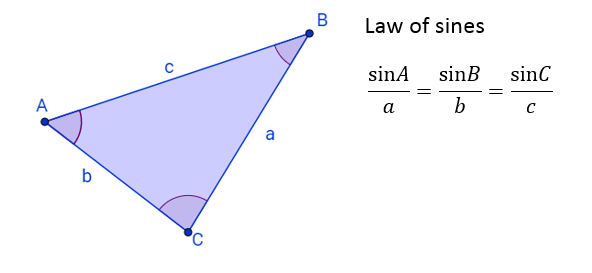
The law of sines states that
We can also write the law of sines or sine rule as:
The Law of Sines is also known as the sine rule, sine law, or sine formula. It is valid for all types of triangles: right, acute or obtuse triangles.
The Law of Sines can be used to compute the remaining sides of a triangle when two angles and a side are known (AAS or ASA) or when we are given two sides and a non-enclosed angle (SSA).
We can use the Law of Sines when solving triangles. Solving a triangle means to find the unknown lengths and angles of the triangle. If we are given two sides and an included angle (SAS) or three sides (SSS) we will use the Law of Cosines to solve the triangle.
Law of Sines: Given Two Angles And One Side
We will first consider the situation when we are given 2 angles and one side of a triangle.
Example:
Solve triangle PQR in which ∠P = 63.5° and ∠Q = 51.2° and r = 6.3 cm.
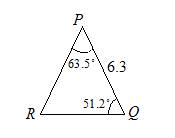
Solution:
First, calculate the third angle.
∠ R = 180° – 63.5° – 51.2° = 65.3°
Next, calculate the sides.

∠ R = 65.3°, p = 6.21 cm and q = 5.40 cm
Law of Sines: Given Two Sides And An Obtuse Angle
We will now consider the situation when we are given two sides and an obtuse angle of a triangle.
Example:
Solve ∆ PQR in which ∠ P =116°, p = 8.3 cm and q = 5.4 cm.
Solution:
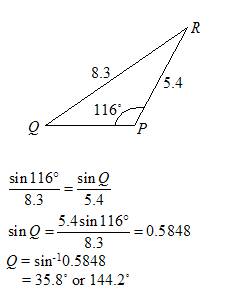
Q cannot be an obtuse angle because the sum of angles in the triangle will exceed 180˚. The only valid value for Q is 35.8˚.
∠ Q = 35.8°, ∠ R = 180° – 116° – 35.8° = 28.2°
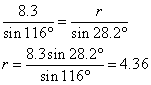
The solution is ∠ Q = 35.8° , ∠ R = 28.2° and r = 4.36 cm
How to solve triangles using Law of Sines?
The Law of Sines
One method for solving for a missing length or angle of a triangle is by using the law of sines.
The law of sines, unlike the law of cosines, uses proportions to solve for missing lengths.
The ratio of the sine of an angle to the side opposite it is equal for all three angles of a
triangle. The law of sines works for any triangle, not just right triangles.
Law of Sines - Ambiguous Case
We will now consider the situation when we are given two sides and one angle of a triangle.
Ambiguous Case
If you are given two sides and a non-included acute angle and the side facing the given angle
is less than the other side, you would obtain two sets of answers. The solution is said to be ambiguous.
Example:
Solve triangle PQR in which ∠ P = 56°, p = 10 cm and q = 12 cm
Solution:
Notice that we can construct two different triangles from the given information.
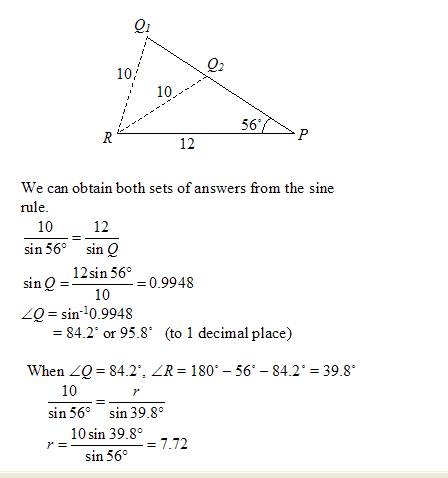
When ∠ Q = 95.8˚, ∠ R = 180˚ – 56˚ – 95.8˚ = 28.2˚
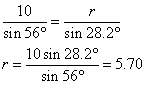
The two sets of solutions are:
∠ Q = 84.2°, ∠ R = 39.8°, r = 7.72 cm
∠ Q = 95.8°, ∠ R = 28.2°, r = 5.70 cm
The ambiguous case when solving triangles using the Law of Sines given SSA
How you may get two solutions when using the Law of Sines?
Law of Sines - No Solution
It is also possible that when given SSA, the triangle does not exists and the Law of Sines will indicate no solution.
Law of Sine - Ambiguous Case (SSA) - No Solution
When given two sides and a non included angle (SSA) in a triangle, this is known as the ambiguous case for Law of Sines. When given these values, you will either have 0, 1, or 2 possible solutions to solve the given triangle.
Law of Sines - SSA - How to tell if there are 0, 1, or 2 solutions
How to use the Law of Sines to tell if there are 0, 1, or 2 solutions.
Proof for the Law of Sines
The following video will show a proof for the law of sines.
The proof of the Law of Sines
Applications using the Law of Sines
This video solves the following application using the law of sines.
Example: Standing on the back of a canyon, a surveyor notices a tree at a bearing of 115°. Then, the surveyor walks 300 meters. The bearing of the tree is then 85°. What is the distance across the canyon?
Application using the law of sines
Example:
A group of forest rangers were hiking through Denali National Park towards Mt. McKinley,
the tallest mountain in North America. From their campsite, they can see Mt. McKinley, and
the angle of elevation from their campsite to the summit is 21°. They know that the
slope of the mountain forms a 127° angle with the ground and that the vertical height
of Mt. McKinley is 20,320 feet. How far away is their campsite from the base of the mountain?
If they can hike 2.9 miles in an hour, how long will it take them to get to the base?
A word problem that involves using the law of sines
Example:
A person has a kite out on 1750 ft of string at an angle of 75° with ground. An observer
notes that the angle formed by the kite and the flier is 102°. How far is the kite from
the observer?
How to solve a word problem that involves using the Law of Sines?
Example:
You are on a hill and can see two building in the distance. Suppose the buildings are six miles
apart. If you are 3.2 miles from one building and the angle between the two lines of sight to
the buildings is 30° 30’, how far are you from the second building?
An application problem that involves using the Law of Sines
Example:
Two wires help support a tall pole. One wire forms an angle of 48° with the ground and the
other wire forms an angle of 72° with the ground. The wires are 20m apart. How far is the pole?
Try the free Mathway calculator and
problem solver below to practice various math topics. Try the given examples, or type in your own
problem and check your answer with the step-by-step explanations.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.