Vector Magnitude
In these lessons, we will learn how to find the magnitude of 2-dimensional vectors and 3-dimensional vectors.
Related Pages
Vectors
Equal Vectors
Vector Multiplication
Vector Geometry
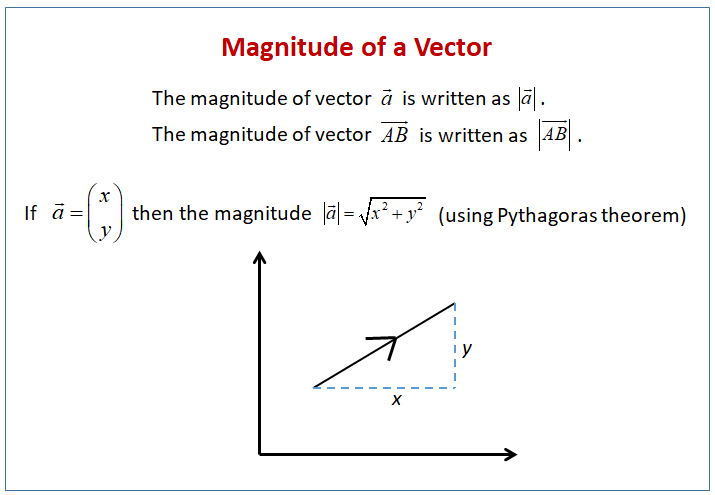
The length of a vector is called the magnitude or modulus of the vector.
The following diagram shows the magnitude of a vector. Scroll down the page for more
examples and solutions to calculate the magnitude of 2-D and 3-D vectors .
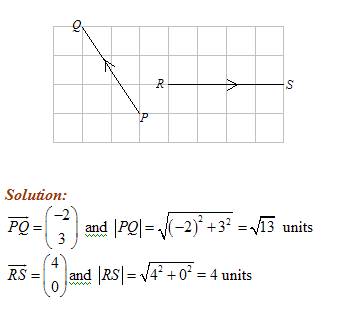
Example:
Express each of the following vectors as a column vector and find its magnitude.
Vectors in 2D
Adding vectors geometrically, scalar multiplication, how to find the magnitude and direction angle of a vector.
A vector with initial point at the origin and terminal point at (a, b) is written <a, b>.
Geometrically, a vector is a directed line segment, while algebraically it is an ordered pair.
Example:
Find the magnitude and the direction angle for u = <-3, 4>
Vectors: magnitude of a vector in 2D.
Example:
Find the magnitude of the following vectors:
a = 4i - 3j
b = -2i + 5j
Vectors in 3D
The following diagram shows how to find the magnitude of a 3D Vector.

A vector can also be 3-dimensional.
The following video gives the formula, and some examples of finding the magnitude,
or length, of a 3-dimensional vector.
Example:
Find the magnitude:
a = <3, 1, -2>
b = 5i -j + 2k
Vectors : Magnitude of a vector 3D.
Examples:
- Find the magnitude of a = 4i + 3j + 2k
- If A(3, -5, 6) and B(4, 1, 3) find the length AB.
Try the free Mathway calculator and
problem solver below to practice various math topics. Try the given examples, or type in your own
problem and check your answer with the step-by-step explanations.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.