

What is a Vector?
Related Topics:
More Lessons on Vectors
Scalar quantities are quantities that have only magnitudes such as time, area and distance.
Vector quantities are quantities that have both magnitudes and directions such velocity (speed and direction), force and acceleration.
A vector can be represented by a directed line segment, whose direction is given by the arrow and the length shows the magnitude of the vector.
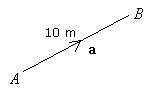
The vectors can be denoted by ![]() or AB or
or AB or ![]() or
or ![]() or a.
or a.
A is called the initial point and B is called the terminal point of ![]() .
.
The magnitude of a vector is the length of the corresponding segment. The magnitude of ![]() is denoted by
is denoted by ![]() .
.
A vector can be written as an ordered pair called a column vector
Consider the line PQ in the diagram. The line represents the translation of P to Q, which is 2 right and 3 up.
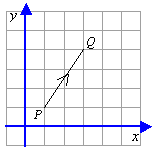
This can be written as the ordered pair

Example:
Express ![]() as a column vector.
as a column vector.
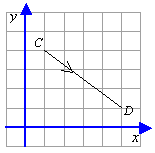
Solution:
The translation of C to D is 4 right and 3 down.
![]()
Videos
An introduction to vectorsThis video introduces vectors - what they are and how they are expressed.
Magnitude, direction, graphing/mapping, Unit Vectors. A video revising vectors at higher GCSE Maths level
Vectors with numbers
Magnitude of a Vector
Algebraic Vectors
Parallel Vectors
Try the free Mathway calculator and
problem solver below to practice various math topics. Try the given examples, or type in your own
problem and check your answer with the step-by-step explanations.



We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.