Solving Systems of Equations by Substitution
Related Pages
Solve Systems of Equations by Addition
Systems of Equations (Graphical Method)
Worksheets to practice solving systems of equations
More Algebra Lessons
These algebra lessons, with videos, examples and step-by-step solutions, introduce the technique of solving systems of equations by substitution.
In some word problems, we may need to translate the sentences into more than one equation. If we have two unknown variables then we would need at least two equations to solve the variable. In general, if we have n unknown variables then we would need at least n equations to solve the variable.
The substitution method is a way to solve systems of linear equations. A system of linear equations is a set of two or more linear equations that contain the same variables. The goal when solving a system of equations is to find the values of the variables that make all of the equations true.
The following example show the steps to solve a system of equations using the substitution method. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions.
In the Substitution Method, we isolate one of the variables in one of the equations and substitute the results in the other equation. We usually try to choose the equation where the coefficient of a variable is 1 and isolate that variable. This is to avoid dealing with fractions whenever possible. If none of the variables has a coefficient of 1 then you may want to consider the Addition Method or Elimination Method.
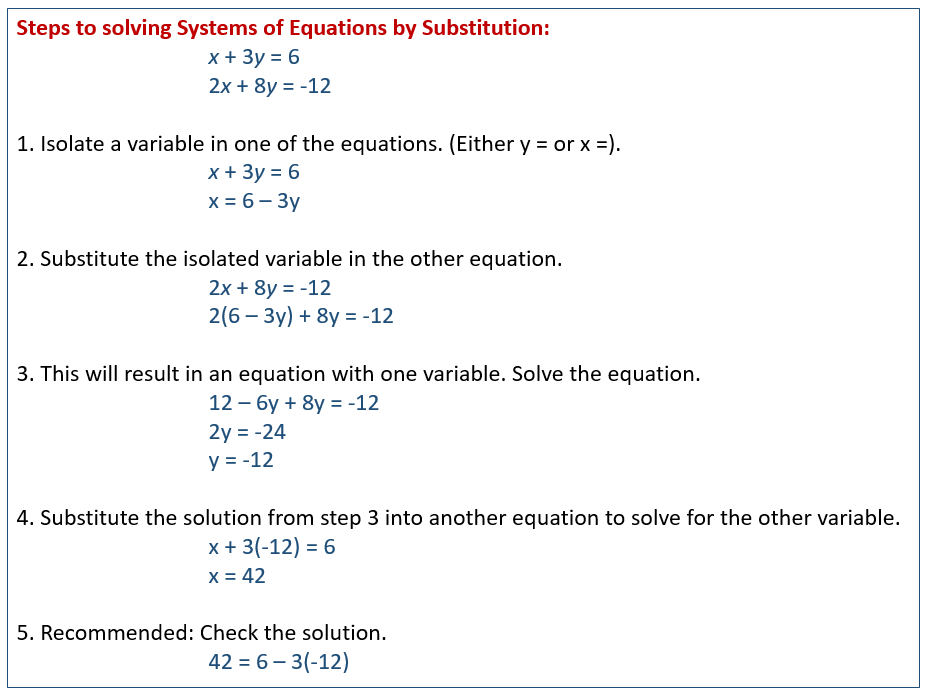
Steps to solving Systems of Equations by Substitution:
- Choose one of the equations and isolate one of the variables on one side of the equation. It’s often easiest to choose an equation where one of the variables has a coefficient of 1 or -1, as this avoids fractions.
- Take the expression you found in step 1 and substitute it for the corresponding variable in the other equation. This will result in an equation with only one variable.
- Solve the equation you obtained in step 2 for the remaining variable.
- Once you have the value of one variable, substitute it back into either of the original equations (or the equation you rearranged in step 1) to find the value of the other variable.
- The solution to a system of two variables is typically written as an ordered pair (x, y).
- Check your answer. Substitute your solution back into both original equations to verify that it makes both equations true.
Note:
- If, when you substitute, you get a false statement (e.g., 2 = 5), the system has no solution.
- If you get a true statement (e.g., 0 = 0), the system has infinitely many solutions.
Example:
3x + 2y = 2 (equation 1)
y + 8 = 3x (equation 2)
Solution:
Step 1: Try to choose the equation where the coefficient of a variable is 1.
Choose equation 2 and isolate variable y
y = 3x - 8 (equation 3)
Step 2: From equation 3, we know that y is the same as 3x - 8
We can then substitute the variable y in equation 1 with 3x - 8
3x + 2(3x - 8) = 2
Step 3: Remove brackets using distributive property
3x + 6x - 16 = 2
Step 4: Combine like terms
9x - 16 = 2
Step 5: Isolate variable x
9x = 18
![]()
Step 6: Substitute x = 2 into
equation 3 to get the value for y
y = 3(2) - 8
y = 6 - 8 = -2
Step 7: Check your answer with equation 1
3(2) + 2(-2) = 6 - 4 = 2
Answer: x = 2 and y = -2
Solving systems of equations using Substitution Method through a series of mathematical steps to teach students algebra
Example:
2x + 5y = 6
9y + 2x = 22
How to solve systems of equations by substitution?
Example:
y = 2x + 5
3x - 2y = -9
Steps to solve a linear system of equations using the substitution method
Example:
x + 3y = 12
2x + y = 6
Example of a system of equations that is solved using the substitution method.
Example:
2x + 3y = 13
-2x + y = -9
Solving Linear Systems of Equations Using Substitution
Include an explanation of the graphs - one solution, no solution, infinite solutions.
Examples:
2x + 4y = 4
y = x - 2
x + 3y = 6
2x + 6y = -12
2x - 3y = 6
4x - 6y = 12
Example of how to solve a system of linear equation using the substitution method.
x + 2y = -20
y = 2x
Try the free Mathway calculator and
problem solver below to practice various math topics. Try the given examples, or type in your own
problem and check your answer with the step-by-step explanations.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.