Applications of Algebra
These lessons are part of a series of lessons for the quantitative reasoning section of the GRE revised General Test. In this lesson, we will learn:
- Applications of Algebra
- Translating Words to Algebra
- Examples of using Algebra to solve Word Problems
- Average Word Problems
- Mixture Word Problems
- Distance, Rate, Time Word Problems
- Work Word Problems
- Word Problems that involve Simultaneous Equations
- Word Problems that involve Inequalities
Related Pages
More Lessons for GRE Math
Math Worksheets
Applications of Algebra
Translating verbal descriptions into algebraic expressions is an essential initial step in solving word problems.
Some examples are given below.
- If the square of the number x is multiplied by 4, and then 15 is added to that product, the result can be represented by 4x2 + 15
- If Peter’s present salary s is increased by 15 percent, then his new salary is 1.15s.
- If y gallons of orange juice are to be distributed among 5 people so that one particular person gets 1 gallon and the rest of the juice is divided equally among the remaining 4, then each of those 4 people will get (y − 1) ÷ 4
This video shows how to translate words and expressions into algebraic expressions involving variables.
Examples of using algebraic techniques to solve word problems
We will now show some examples of using algebraic techniques to solve word problems. More examples of algebra word problems can be found here.
Average Word Problems The following are examples of word problems that involve the average or arithmetic mean.
Example 1:
Ellen has received the following scores on 3 exams: 82, 74, and 90. What score will
Ellen need to receive on the next exam so that the average (arithmetic mean) score for the 4 exams will be 85?
Let x represent the score on Ellen’s next exam.
The average of the 4 exams is
![]()
Solving for x we get
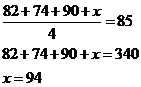
Therefore, Ellen will need to attain a score of 94 on the next exam.
Example 2:
On her first four games Jennifer bowled 101, 112, 126, 108. What is the minimum score she must bowl in her fifth game in order to have an average of at least 110?
Mixture Word Problems
The following are some examples of word problems that involve mixture and concentration of mixture.
Example 1:
A mixture of 12 ounces of vinegar and oil is 40 percent vinegar, where all of the
measurements are by weight. How many ounces of oil must be added to the mixture to produce a new mixture that is only 25 percent vinegar?
Let x represent the number of ounces of oil to be added. Then the total number of ounces of the new mixture will be 12 + x, and the total number of ounces of vinegar in the new mixture will be (0.40)(12). Since the new mixture must be 25 percent vinegar, we get
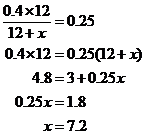
7.2 ounces of oil must be added to produce a new mixture that is 25 percent vinegar.
Example 2:
A solution contains 15% hydrochloric acid. How much water should be added to 50 ml of this solution to dilute it to a 2% solution?
Distance, Rate, Time Word Problems
The following are some examples of distance, rate, time word problems.
Example 1:
In a driving competition, Jeff and Dennis drove the same course at average speeds of 51
miles per hour and 54 miles per hour, respectively. If it took Jeff 40 minutes to drive the course, how long did it take Dennis?
Let x be the time, in minutes, that it took Dennis to drive the course. The distance d, in miles, is equal to the product of the rate r, in miles per hour, and the time t, in hours; that is, d = rt
Note that since the rates are given in miles per hour, it is necessary to express the times in hours; for example, 40 minutes equals ![]() of an hour.
of an hour.
Using the formula, d = rt, we can get the following table.
|
Distance |
Rate |
Time |
Jeff |
51 × |
51 |
|
Dennis |
54 × |
54 |
|
Since the distances are equal,
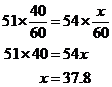
It took Dennis approximately 37.8 minutes to drive the course.
An introduction to solving word problems on uniform motion (rate-time-distance) using the formula rate x time = distance, or rt=d.
Example:
Two cyclists start at the same corner and ride in opposite directions. One cyclist rides twice as fast as the other. In 3 hours, they are 81 miles apart. Find the rate of each cyclist. Answer: 9 mph and 18 mph.
Word problem using uniform motion rt=d formula
Example:
A jogger started running at an average speed of 6 mph. Half an hour later, another runner started running after him starting from the same place at an average speed of 7 mph. How long will it take for the runner to catch up to the jogger? Answer: 3 hours.
Word problem using uniform motion rt=d formula
Example:
A 555-mile, 5-hour trip on the Autobahn was driven at two speeds. The average speed of the car was 105 mph on the first part of the trip, and the average speed was 115 mph for the second part. How long did the car drive at each speed? Answer: 105 mph for 2 hours and 115 mph for 3 hours.
Word problem using uniform motion rt=d formula
Example:
Andy and Beth are at opposite ends of a 18-mile country road with plans to leave at the same time running toward each other to meet. Andy runs 7 mph while Beth runs 5 mph. How long after they begin will they meet? Answer: 1.5 hours.
Example:
A car and a bus set out at 2 pm from the same spot, headed in the same direction. The average speed of the car is twice the average speed of the bus. After 2 hours, the car is 68 miles ahead of the bus. Find the rate of the bus and the car. Answer: Bus speed: 34 mph; Car speed: 68 mph.
Example:
A pilot flew from one city to another city averaging 150 mph. Later, it flew back to the first city averaging 100 mph. The total flying time was 5 hours. How far apart are the cities? Answer: 300 miles.
Work Word Problems
The following are some examples of word problems that involve work done by individuals or machines.
Example:
It takes Maria ten hours to pick forty bushels of apples. Kayla can pick the same amount in 12 hours. How long would it take them if they worked together?
Word Problems Involving Work
Examples:
- It takes an experienced painter 6 days to paint a house. It takes an apprentice 8 days to paint the same house. How long would it take if they worked together?
- One pipe can fill a tank in 8 hours. Another pipe can empty the tank in twelve hours. If both pipes are opened simultaneously, how long will it take to fill the tank?
Applications that involve Systems of Equations
The following are examples of applications that involve systems of equations or solving simultaneous equations.
Examples:<
- Find two numbers for which the sum is 93 and the difference is 9.
- The perimeter of a rectangle is 160 yd. The width is 4 more than half the length. Find the length and the width.
- Sunset rents a 18 ft truck for $49.95 plus 75 cents per mile. Cactus rents a 18 ft van for $59.95 plus 50 cents per mile. For what mileage is the cost the same?
Examples:
- Assume all Pheonix College courses are either worth 3 or 4 credits. The cross country team is taking a total of 40 courses that are worth 144 credits. How many 3-credit courses and how many 4-credit courses are being taken?
- HomeMart charges $3.50 for a CFL light bulb and Supply Depot charges $2.50 for a CFL light bulb that doesn’t las quite as long. If your apartment complex lost the invoice, but they knew they purchased 300 bulbs and spent $885, how many bulbs were purchased from each store.
- Grounds Works charges $8.00/lb for premium roast coffee and $4.50/lb for value roast coffee. How much of each type should be used to make a 10lb blend that would cost $5.90/lb?
- A train leave Prescott, AZ and travels north to Grand Canyon at a speed of 25mph. One and a half hour later, an express train leaves on a parallel track and travels north at 60mph. How far from the starting station will they meet?
Applications that involve inequalities
The following are examples of algebra word problems that involve inequalities
Examples:
- Andrea has $53.50 in her pocket and wants to purchase shirts at a sale price of $14.95 each.
What is the greatest number of shirts she can buy? (Assume that the shirts are exempt from sales tax) - Three times a number increased by 8 is at most 40. Find the greatest possible value of the number.
- The length of a rectangle is 8 meters less than 5 times its width. If the perimeter of the rectangle is at most 104 meters, find the greatest possible width of the rectangle.
- Two consecutive numbers are such that their sum is greater than 98 decreased by twice the larger. Find the smallest possible values foe the integers.
Example:
A widget factory has a fixed operating cost of $3,600 per day plus costs $1.40 per widget produced. If a widget sells for $4.20, what is the least number of widgets that must be sold per day to make a profit?
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.