Illustrative Mathematics Unit 6.1, Lesson 10: Bases and Heights of Triangles
Learn about how to identify corresponding bases and heights in any triangle, and use that information to find the area of a triangle. After trying the questions, click on the buttons to view answers and explanations in text or video.
Return to the list of Illustrative Math lessons
Bases and Heights of Triangles
Let’s use different base-height pairs to find the area of a triangle.
Illustrative Math Unit 6.1, Lesson 10 (printable worksheets)
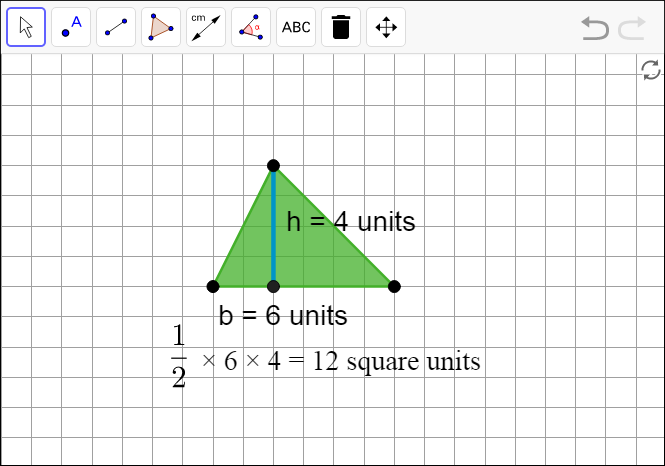
10.1 - An Area of 12
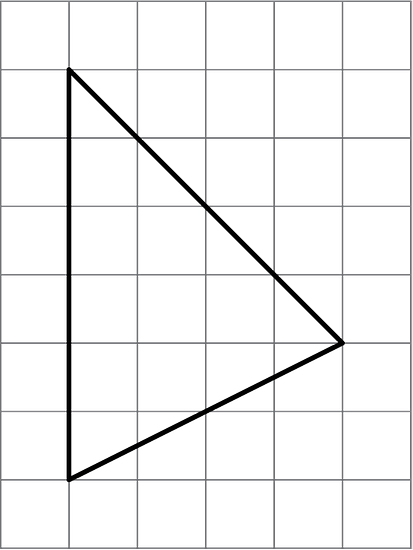
Open the applet. Draw one triangle with an area of 12 square units. Try to draw a non-right triangle. Be prepared to explain how you know the area of your triangle is 12 square units.
-
Hints
There are a number of strategies which you can use.
Can you draw a quadrilateral with an area of 12?
Can you use what you know about parallelograms to help you?
The formula for the area of a triangle is A = ½ · b · h. What pairs of values for b and h will get A = 12?
-
See Possible Answers

The formula for the area of a triangle is A = ½ · b · h.
The area of this triangle is ½ × 6 units × 4 units = 12 square units.Other methods of demonstrating the area of the triangle are possible, as are other triangles with an area of 12 square units.
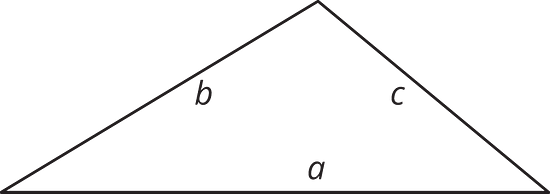
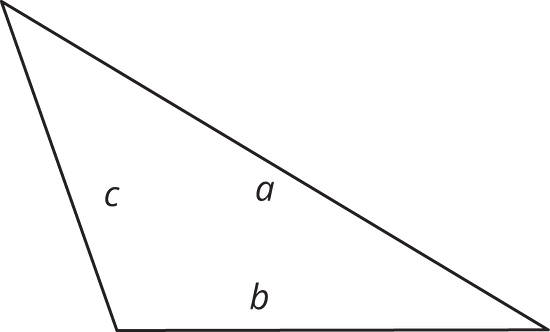
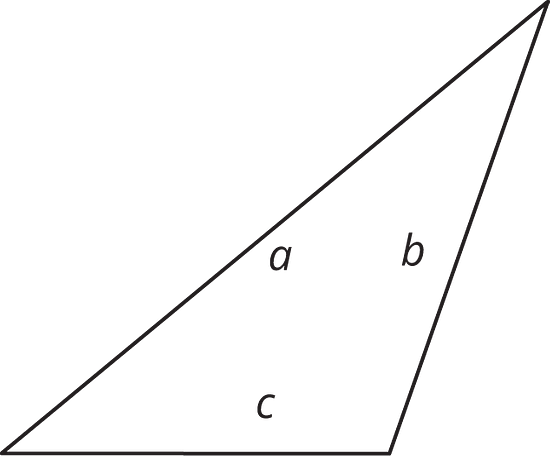
10.2 - Hunting for Heights
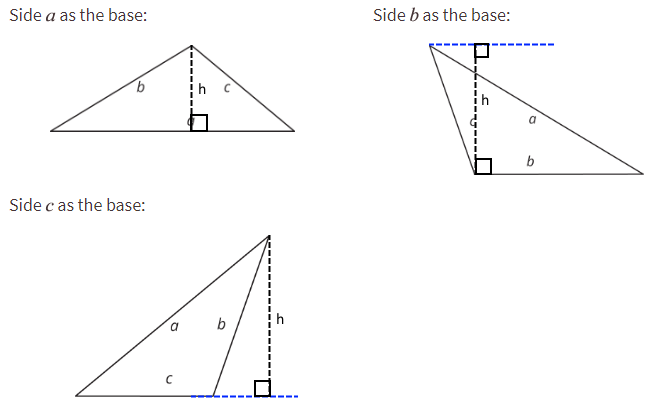
- Here are three copies of the same triangle. The triangle is rotated so that the side chosen as the base is at the bottom and is horizontal. Draw a height that corresponds to each base.
Side a as the base:
Side b as the base:
Side c as the base:
-
Hints
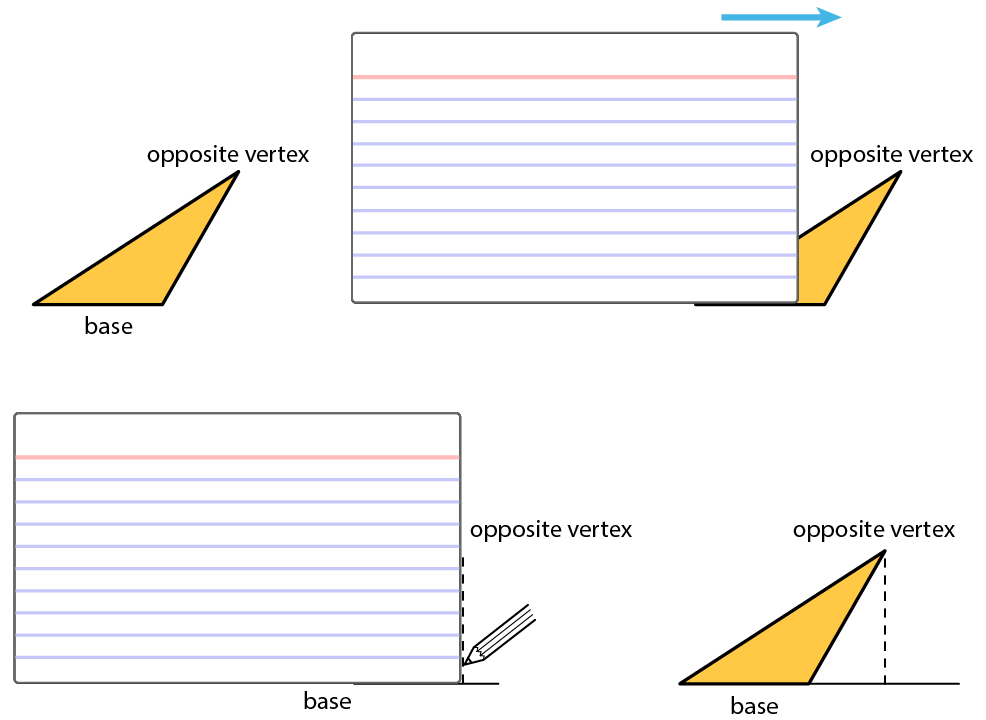
Recall that height is the length of a perpendicular segment from the base to the vertex opposite of it. The opposite vertex is the vertex that is not an endpoint of the base.
A segment showing a height must be drawn at a right angle to the base, but it can be drawn in more than one place. It does not have to go through the opposite vertex, as long as it connects the base and a line that is parallel to the base and goes through the opposite vertex.
-
See Possible Answers

Black dashed lines are the heights corresponding to the chosen base in each of these triangles.
Notice the blue dashed lines. The height must be perpendicular to the base and measure the length between the base and the opposite vertex, but does not need to pass through the base or the opposite vertex itself.
This is similar to how the height of a parallelogram can be drawn.
- Draw a line segment to show the height for the chosen base in each triangle.
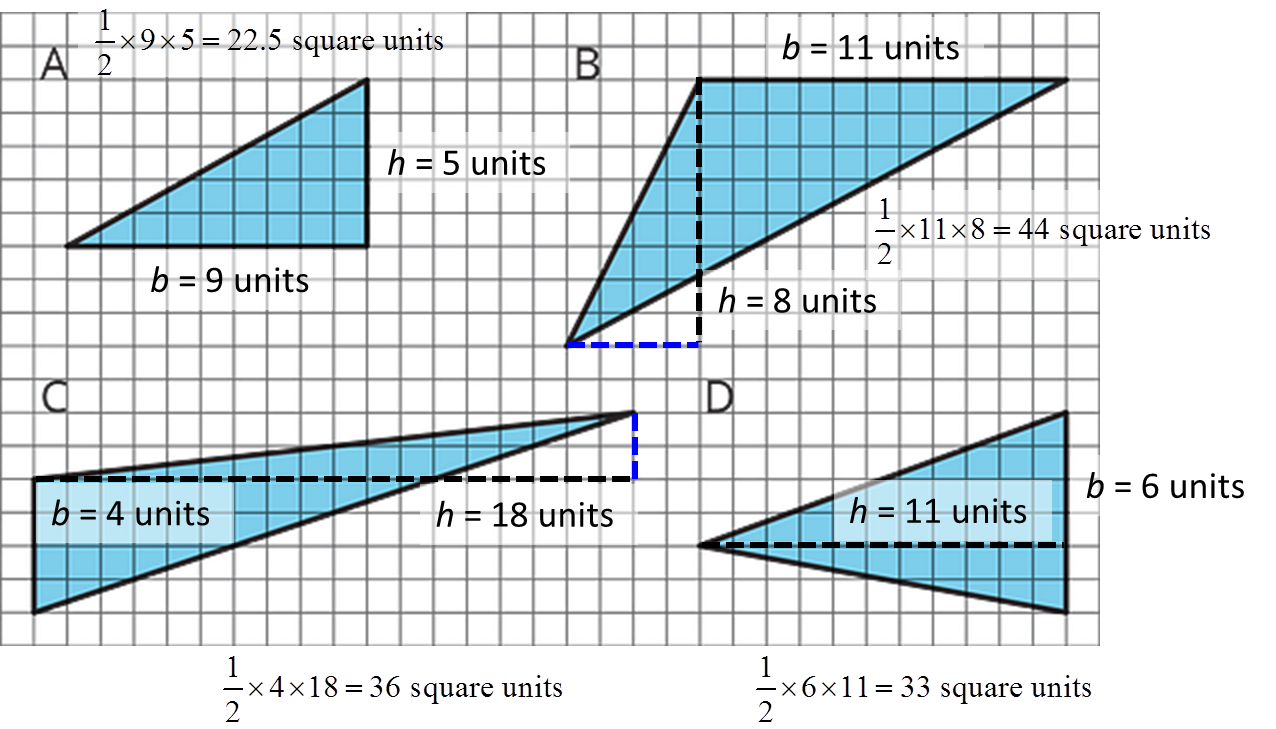
10.3 - Some Bases Are Better Than Others
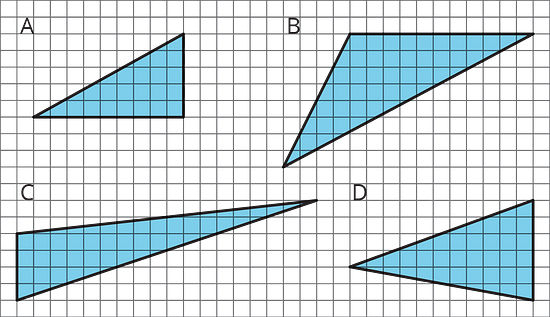
For each triangle, identify and label a base and height. If needed, draw a line segment to show the height.
Then, find the area of the triangle. Show your reasoning. (The side length of each square on the grid is 1 unit.)
-
Hints
To find the area of these triangles, choose a base that will let you count the length of the base and the height.
If you are having difficulty drawing the height, remember that the height does not need to pass through the base or the opposite vertex itself.
-
See Possible Answers

A: ½ × 9 units × 5 units = 22.5 square units
B: ½ × 11 units × 8 units = 44 square units
C: ½ × 4 units × 18 units = 36 square units
D: ½ × 6 units × 11 units = 33 square units
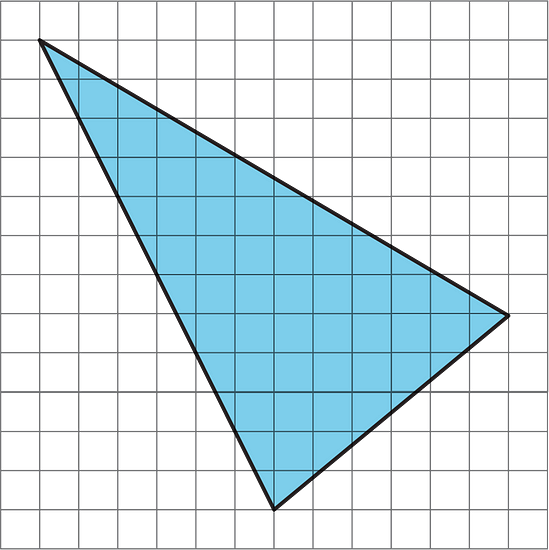
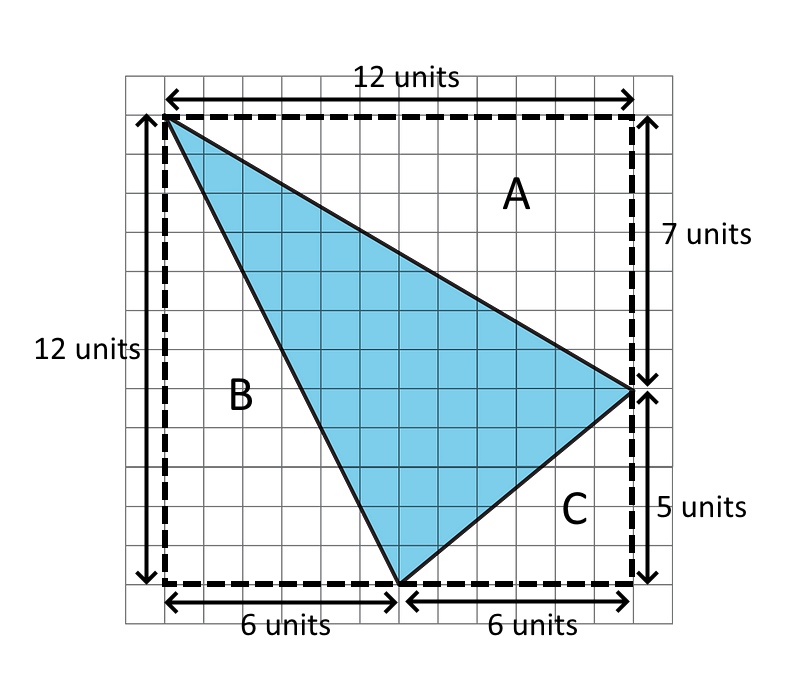
Find the area of the triangle below. Show your reasoning.
-
Hints
You can’t directly count the lengths of any of the sides. What other strategies for finding area do you know? Can this triangle be enclosed in another shape?
-
See Possible Answers

By enclosing this triangle in a square, there are now three unshaded triangles whose bases and heights can be counted.
The total area of the square is 12 units × 12 units = 144 square units.Area of triangle A = ½ × 12 units × 7 units = 42 square units
Area of triangle B = ½ × 6 units × 12 units = 36 square units
Area of triangle C = ½ × 6 units × 5 units = 15 square unitsThe area of the shaded triangle is 144 - (42 + 36 + 15) = 51 square units.
Lesson 10 Summary
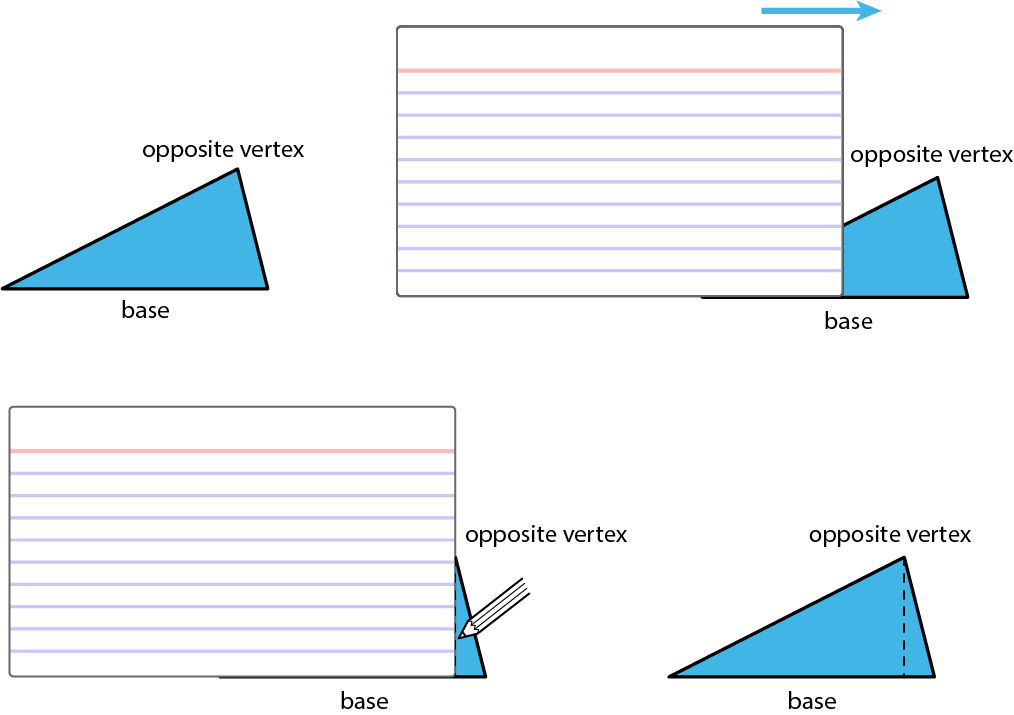
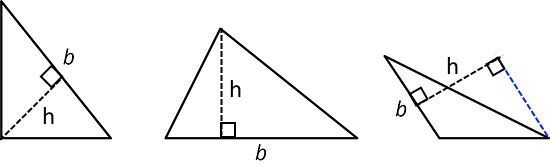
A height of a triangle is a perpendicular segment between the side chosen as the base and the opposite vertex. We can use tools with right angles to help us draw height segments.
An index card (or any stiff paper with a right angle) is a handy tool for drawing a line that is perpendicular to another line.
- Choose a side of a triangle as the base. Identify its opposite vertex.
- Line up one edge of the index card with that base.
- Slide the card along the base until a perpendicular edge of the card meets the opposite vertex.
- Use the card edge to draw a line from the vertex to the base. That segment represents the height. Sometimes we may need to extend the line of the base to identify the height, such as when finding the height of an obtuse triangle, or whenever the opposite vertex is not directly over the base. In these cases, the height segment is typically drawn outside of the triangle.
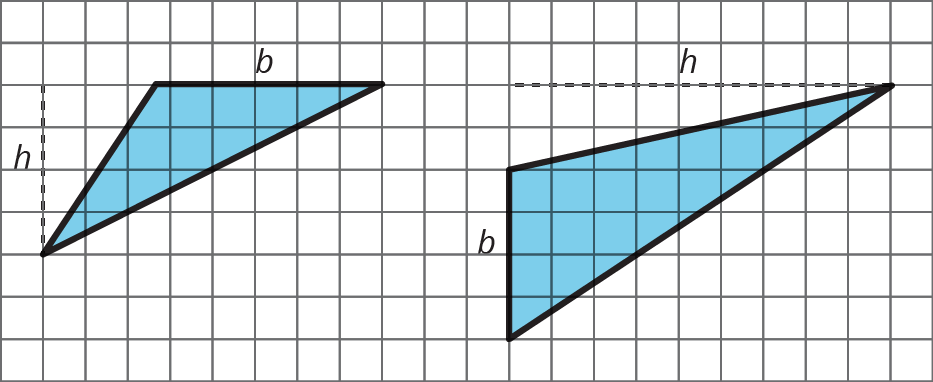
Even though any side of a triangle can be a base, some base-height pairs can be more easily determined than others, so it helps to choose strategically.
For example, when dealing with a right triangle, it often makes sense to use the two sides that make the right angle as the base and the height because one side is already perpendicular to the other.
If a triangle is on a grid and has a horizontal or a vertical side, you can use that side as a base and use the grid to find the height, as in these examples:
Practice Problems
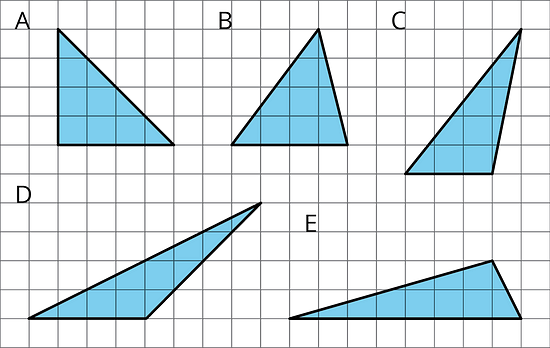
- For each triangle, a base is labeled b. Draw a line segment that shows its corresponding height.
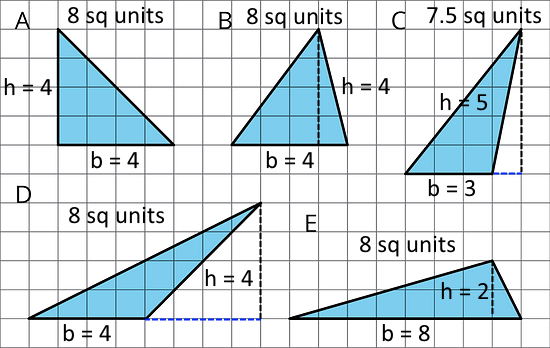
- Select all triangles that have an area of 8 square units. Explain how you know.
-
Show Answers

Area of triangle A = ½ × 4 units × 4 units = 8 square units
Area of triangle B = ½ × 4 units × 4 units = 8 square units
Area of triangle C = ½ × 3 units × 5 units = 7.5 square units
Area of triangle D = ½ × 4 units × 4 units = 8 square units
Area of triangle E = ½ × 8 units × 2 units = 8 square units
A, B, D, and E all have an area of 8 square units. C does not.
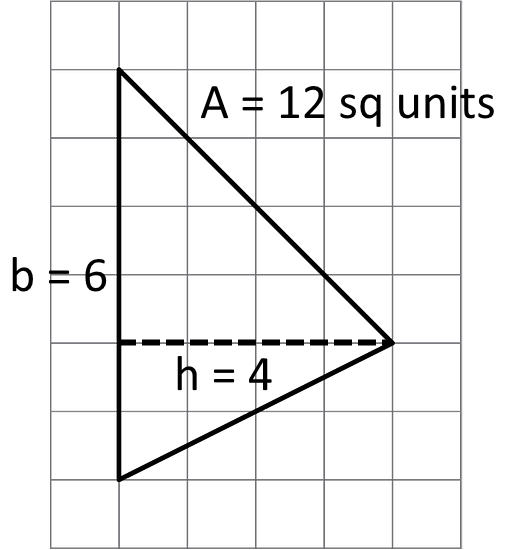
- Find the area of the triangle. Show your reasoning.
If you get stuck, carefully consider which side of the triangle to use as the base.
-
Show Answers

A = ½ · b · h
A = ½ × 6 units × 4 units
A = 12 unitsNote how the base can be any side of the triangle, and that the most useful base is the side that allows you to measure the base and height.
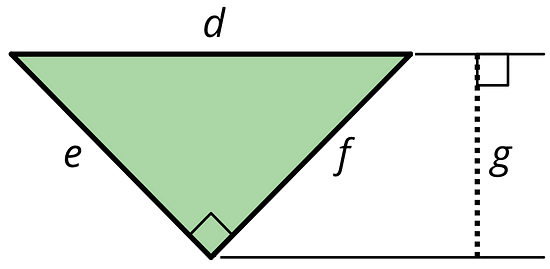
- Can side d be the base for this triangle? If so, which length would be the corresponding height? If not, explain why not.
-
Show Answers
Side d can be the base. Any side of a triangle can be the base.
The corresponding height is g, as it is perpendicular to d, and perpendicular to the line which is parallel to d and passes through the opposite vertex.
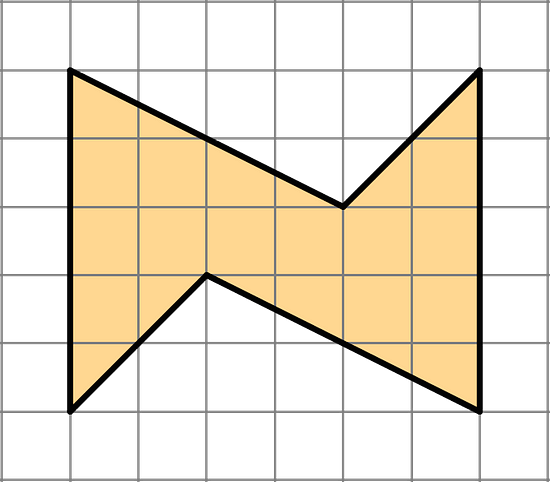
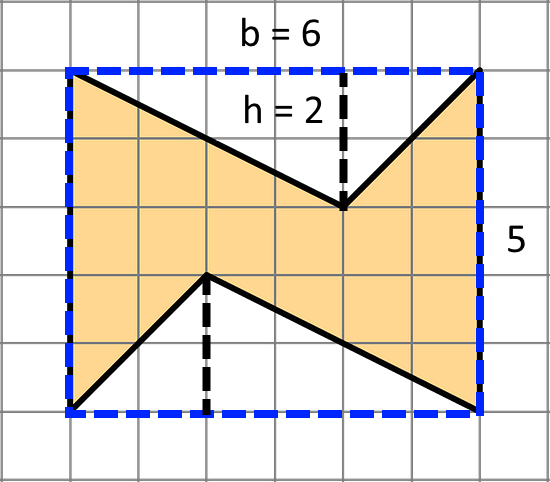
- Find the area of this shape. Show your reasoning.
-
Show Answers

The shape can be enclosed in a rectangle as shown by the blue dashed lines. This rectangle has a total area of 6 units × 5 units = 30 square units.
The two unshaded triangles have a total area of 2 × ½ × 6 units × 2 units = 12 square units.
Hence, the shaded shape has an area of 30 square units - 12 square units = 18 square units.
-
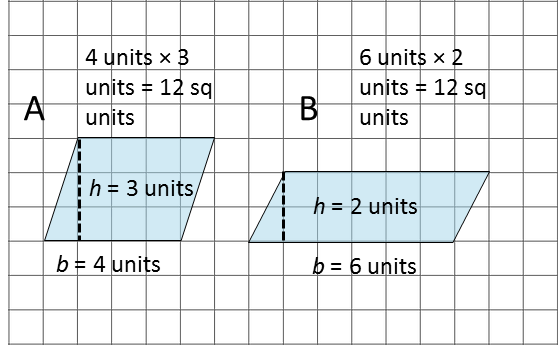
Show Answers

The area of parallelogram A is 4 units × 3 units = 12 square units.
The area of parallelogram B is 6 units × 2 units = 12 square units.
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.