Compound Interest
Related Topics:
More Lessons for GCSE Maths
Math Worksheets
A collection of videos to help GCSE Maths students learn how to calculate compound interest.
Compound interest is a powerful financial concept where interest is calculated not only on the initial principal but also on the accumulated interest from previous periods. This means you earn “interest on interest,” leading to faster growth of your money over time.
The following diagram gives the Compound Interest Rate Formula where the interest is compounded once per year. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions.
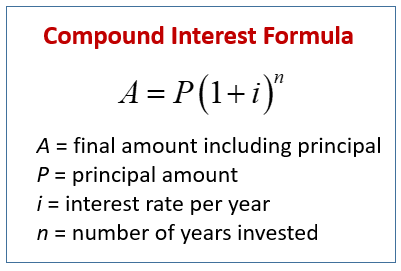
The formula for compound interest is:
A = P (1 + R/n)(nt)
Where:
A = the future value of the investment/loan, including interest
P = the principal investment amount (the initial deposit or loan amount)
R = the annual interest rate (as a decimal)
n = the number of times that interest is compounded per year
t = the number of years the money is invested or borrowed for
If the interest is compounded once a year (n = 1) then the formula simplifies to:
A = P (1 + R)(t)
Steps to Calculate Compound Interest
- Identify the Given Values:
Determine P, r, n, and t. - Convert the Interest Rate:
If the interest rate is given as a percentage, convert it to a decimal by dividing by 100. - Plug Values into the Formula:
Substitute P, r, n, and t into the formula:
A = P (1 + R/n)(nt) - Calculate the Total Amount:
Perform the calculations to find A. - Calculate the Interest Earned:
Subtract the principal from the total amount:
I=A−P.
Compound interest
Examples:
- Dan has £6,000 in his bank account. His bank account pays compound interest at a rate of 4% per year. How much will Dan have after 3 years?
- Dan has £5,489.23 in his bank account at 1 Jan 2015. His bank account pays compound interest at a rate of 2.89% per year. How much will Dan have after 3 years?
- Sarah wants to invest £3,000 for 3 years in the same bank. The Big Bank pays 4% for the first year and 1% each year after. The Big Bank pays 5% for the first year and 0.5% each year after. At the end of 3 years, Sarah wants as much money as possible. Which bank should she invest her £3,000 in?
How to work out compound interest?
GCSE Unit 1 Compound and Simple Interest
Interest Word Problems Worksheets
Interest Problems
Simple Interest Word Problems
Compound Interest Word Problems
Compound Interest & Continuously Compound Interest
Investment Word Problems
Printable & Online Algebra Worksheets
Try the free Mathway calculator and
problem solver below to practice various math topics. Try the given examples, or type in your own
problem and check your answer with the step-by-step explanations.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.