Concave Lens and Ray Diagrams
Related Topics:
IGCSE Physics Lessons
Math Worksheets
Ray Diagrams for Convex Lens
Interactive Ray Diagrams
A series of free GCSE/IGCSE Physics Notes and Lessons.
A ray diagram for a concave lens (diverging lens) is a graphical representation of how light rays diverge (spread out) after passing through the lens. Concave lenses are thinner at the center than at the edges and cause light rays to diverge.
The following diagrams show the ray diagram for a concave lens. With a concave lens, the image will always be diminished, the right way up and virtual.
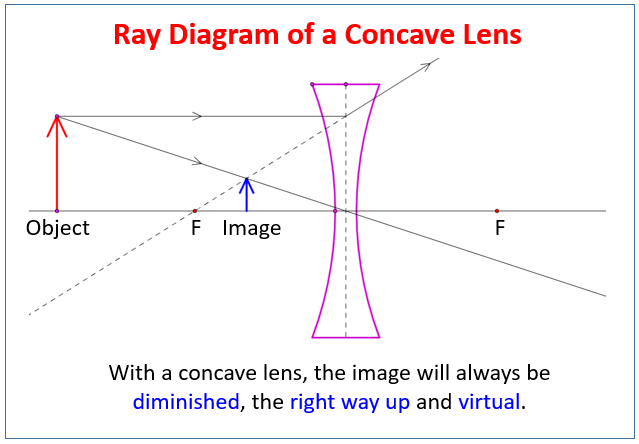
Steps to Draw a Ray Diagram for Concave Lens:
- Draw the Lens and Principal Axis:
Draw a vertical line representing the concave lens.
Draw a horizontal line through the center of the lens, representing the principal axis.
Mark the focal points (F) on both sides of the lens, equidistant from the center. - Draw the Object:
Draw an arrow representing the object, placed in front of the lens. - Draw Ray 1 (Parallel Ray):
Draw a ray from the top of the object parallel to the principal axis, traveling towards the lens.
At the lens, draw the refracted ray diverging upwards, as if it originated from the focal point on the same side of the lens.
Use a dashed line to extend this refracted ray back to the focal point. - Draw Ray 2 (Center Ray):
Draw a ray from the top of the object straight through the center of the lens. - Locate the Image:
The point where the dashed extension of Ray 1 and Ray 2 intersect is where the top of the image is located.
Draw the image as an arrow from the principal axis to this intersection point. - Image Characteristics:
The image formed by a concave lens is always:
Virtual (formed by the extensions of rays).
Upright.
Diminished (smaller than the object).
Formed on the same side of the lens as the object.
Ray Diagrams: Diverging Lenses
A diverging lens (also known as a concave lens) is one that causes light passing through it to diverge away from a focus. This can result in the formation of a virtual image. This video explains the rules that can used to draw lens ray diagrams for diverging lenses and demonstrate the construction of one such diagram.
Ray Tracing for Concave or Diverging Lens
Draw different ray diagrams with the object at different places in relation to the focus and find out where the image appears.
Concave Lenses
Draw a ray diagram to show how an image is formed by a concave lens.
Describe the properties of an image produced by a concave lens.
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.