Dilation Transformation
Related Pages
Plane Transformations
More Geometry Lessons
Transformation Games
In these lessons, we will learn
- what is dilation or enlargement and reduction?
- dilation with scale factor greater than 1.
- dilation with scale factor between 0 and 1.
- dilation with a negative scale factor.
- dilation on the coordinate plane.
What is Dilation or Enlargement?
A dilation is a transformation that produces an image that is the same shape as the original, but is a different size. (The image is similar to the original object). Dilation is a transformation in which each point of an object is moved along a straight line. The straight line is drawn from a fixed point called the center of dilation. The distance the points move depends on the scale factor. The center of dilation is the only invariant point.
Scale factor = ![]()
If the scale factor is greater than 1, the image is an enlargement.
If the scale factor is between 0 and 1, the image is a reduction.
If the scale factor is 1, the image remains the same size (identity transformation)
If the scale factor is less than 0, the image is also reflected through the center of dilation.
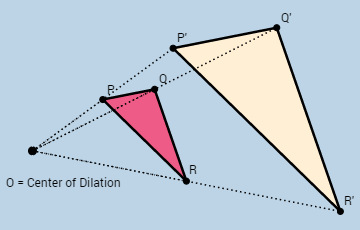
Example:
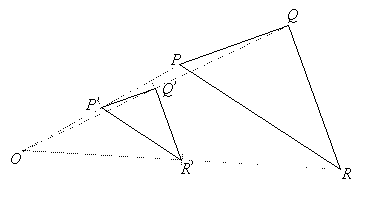
The figure shows two similar triangles PQR and P’Q’R’. Triangle P’Q’R’ is a dilation of triangle PQR. We say that triangle PQR is transformed onto triangle P’Q’R’ by a dilation with center at O and scale factor ![]()
The following diagrams show the triangle ABC dilated with different scale factors. Scroll down the page for more examples and explanations of dilations.
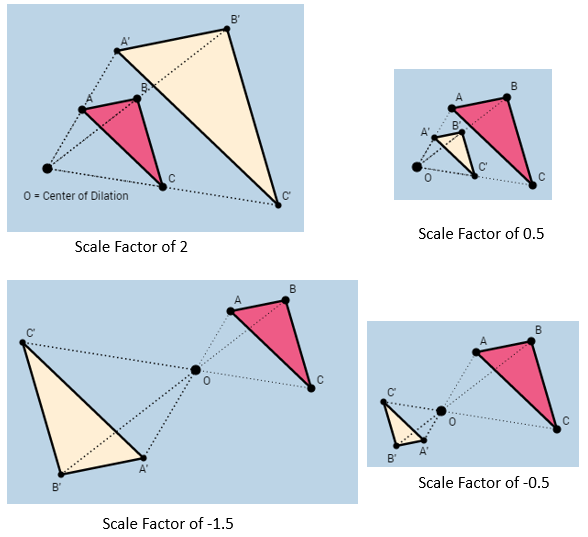
Types of Dilation
- Enlargement (Expansion) When |k| > 1, the image is larger than the original.
- Reduction (Contraction) When 0 < |k| < 1, the image is smaller than the original.
- Negative Scale Factor (Inversion + Scaling) When k < 0, the image is flipped and scaled.
Dilation with scale factor > 1
We will first look at enlargements which are dilations with scale factors greater than 1
Example:
Enlarge triangle PQR with O as the center of dilation and a scale factor of 2.
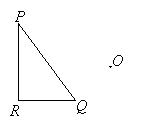
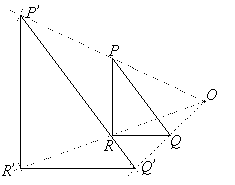
Solution:
Step 1: Measure OP.
Step 2: Extend the line OP to the point P’ such that OP’ = 2OP.
Step 3: Repeat the steps for all the vertices: point Q to get Q’ and point R to get R’.
Step 4: Join the points P’Q’R’ to form the image.
Example:
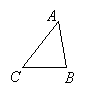
Enlarge triangle ABC with C as the center of dilation and a scale factor of 3.
Solution:
Step 1: Measure CA.
Step 2: Extend the line CA to the point A’ such that CA’ = 3CA.
Step 3: Repeat the steps for point B to get B’.
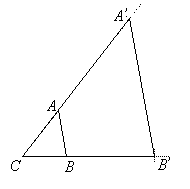
Note that in this example, all the points in the triangle have been transformed except point C, which is the only invariant point.
Example:
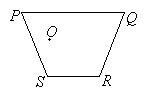
Draw an image of the figure PQRS. O is the center of dilation and the scale factor is 1.5.
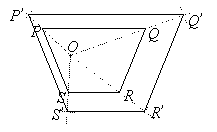
Solution:
Step 1: Join OP.
Step 2: Extend the line OP to OP’, such that OP’ = 1.5 × OP
Step 3: Repeat for all the other vertices Q, R and S.
Step 4: Join P’, Q’, R’ and S’ to form the image.
An introduction to the concepts of dilation transformations
What happens when the scale factor or the center of the dilation is changed?
Dilation with scale factor between 0 and 1
If the scale factor of a dilation is between 0 and 1, the image will be smaller than the object. It is then called a reduction.
Example:
Enlarge triangle PQR with O as the center of enlargement and scale factor ![]() .
.
Solution:
Step 1 : Join O to P.
Step 2 : Mark off the point P ’ on OP such that OP’ = ![]() OP.
OP.
Step 3 : Repeat the steps for all the vertices: point Q to get Q’ and point R to get R’
Step 4 : Join the points P’Q’R’ to form the image.
Dilation of a Geometric Figure
How to create a dilation of a geometric figure using a center of dilation and a scale factor of half?
Dilation with a Negative Scale Factor
If the scale factor of a dilation is negative then the image will be on the opposite side of the center of dilation compared with the object.
How to create a dilation of a geometric figure using a center of dilation and a negative scale factor?
Dilation on the Coordinate Plane
We will now look at how to create a dilation on a coordinate plane.
If a figure is dilated with a center of dilation at the origin (0, 0) and a scale factor k, the coordinates of each point (x, y) on the original figure are transformed to (kx, ky) on the image.
Formula: (x’, y’) -> (kx, ky)
If the center is at (a, b), the formula adjusts to:
(x’, y’) -> (a + k(x - a), b + k(y - b))
Dilations
A dilation is a non-rigid transformation, which means that the original and the image are not congruent. They are, however, similar figures.
To perform dilations, a scale factor and a center of dilation are needed. If the scale factor is larger than 1, the image is larger than the original; if the scale factor is less than 1, the image is smaller than the original.
How to get the scale factor given the points of the shape and its image?
Try the free Mathway calculator and
problem solver below to practice various math topics. Try the given examples, or type in your own
problem and check your answer with the step-by-step explanations.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.