Directed Numbers
Related Pages
Directed Numbers Worksheet
More GCSE Maths Lessons
Math Worksheets
These lessons help GCSE/IGCSE Maths students learn about directed numbers and how to perform operations on directed numbers.
Directed numbers are numbers with a sign (+ or -) that indicate their direction or position relative to zero. These numbers are used in real-world contexts like temperature, money (debt/savings), elevation (above/below sea level), and time zones.
How to add and subtract directed numbers?
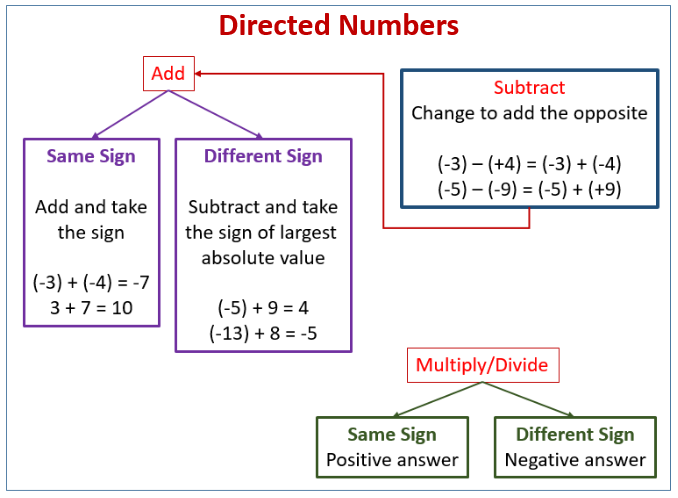
Rule 1: If the signs are the same then add the numbers and keep the original sign.
Rule 2: If the signs are different then subtract: Big number minus small number. Keep the sign of the big number.
How to multiply and divide directed numbers?
Rule 1: The answer is positive when all the numbers are positive or when there is an even number of negative signs in the problem.
Rule 2: The answer is negative when there is an odd number of negative signs in the problem.
The following diagram gives the rules for the addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of directed numbers. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions on the operations for directed numbers.
Directed Numbers Worksheets
Practice your skills using the following worksheets:
Printable & Online Integer Worksheets
Directed Numbers Adding and Subtracting
Directed Numbers Multiplying and Dividing
Rules for adding, subtracting, multiplying and dividing positive and negative numbers
GCSE Maths - Negative Numbers (Adding, Subtracting,Multiplying, Dividing)
Real-life Applications of Directed Numbers:
- Temperature: Temperatures above zero are positive (e.g., +25°C), while temperatures below zero are negative (e.g., -5°C).
- Money: Having money is represented by a positive number (e.g., +$100), while owing money or being in debt is represented by a negative number (e.g., -$50).
- Elevation: Heights above sea level are positive (e.g., +150m), and depths below sea level are negative (e.g., -30m).
- Direction/Distance: Moving in one direction can be positive (e.g., +5 km east), while moving in the opposite direction is negative (e.g., -3 km west).
- Financial Transactions: Credits to an account can be positive, and debits can be negative.
How to Avoid Mistakes:
Memorize the sign rules for addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
Always follow the order of operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS).
Read word problems carefully and think about the context.
Be extra careful when working with negative numbers.
Double-check your work.
Practice regularly. The more you work with directed numbers, the more comfortable you’ll become.
Try the free Mathway calculator and
problem solver below to practice various math topics. Try the given examples, or type in your own
problem and check your answer with the step-by-step explanations.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.