Distance-time Graphs
A series of free Science Lessons for 7th Grade and 8th Grade, KS3 and Checkpoint Science in preparation for GCSE and IGCSE Science.
The following diagram shows examples of distance-time graphs. Scroll down the page for more examples on how to construct a distance-time-graph.
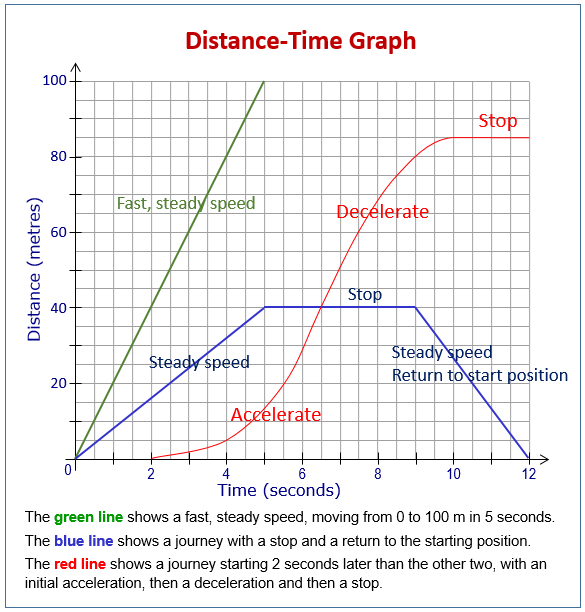
Distance-time graphs
Construct a distance-time graph from given information.
Determine an object’s speed from a distance-time-graph.
Use a tangent to determine the speed of an accelerating object.
Example:
Draw a distance-time-graph of the following:
- A person walked 100m in a straight line in 100s. He then stopped for 40s and then walked another 70m in 50s.
- A person walks in a straight line 60m in 80s. He then walk a further 110m in 70s.
Gradient of a Distance-Time Graph
How to calculate the speed from a distance time graph?
The slope of a distance-time graph is the speed of the object.
Distance Time Graphs
Average Speed = distance/time
Slope of graph = average speed (y-axis = distance, x-axis = time)
- Easy to compare speeds
- The greater the gradient, the greater the speed
Distance-time graphs
Speed = Distance/Time
Example:
- A person walks to a shop 100 meters from their house. This takes 300 seconds. They spend 200 seconds at the shop and then return home in 500 seconds. They spend 200 seconds at the shop and then return home in 500 seconds.
- A motorcyclist leaves home and travels 500 meters in 100 seconds. They then stay in the same place for 300 seconds before traveling home in 200 seconds.
On a distance-time graph, the gradient (steepness) of the line represents the speed. The steeper the line, the faster the speed.
Try the free Mathway calculator and
problem solver below to practice various math topics. Try the given examples, or type in your own
problem and check your answer with the step-by-step explanations.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.