Distance Word Problems (Same Direction)
Related Pages
Rate Distance Time Word Problems
Distance Problems
Average Speed Problems
Distance, rate, and time problems involving traveling at different rates are common in algebra. These problems often involve two or more objects moving at different speeds, either toward each other, away from each other, or in the same direction.
Distance Word Problems (same direction)
Distance problems are word problems that involve the distance an object will travel at a certain average rate for a given period of time.
The formula for distance problems is:
distance = rate × time or
d = r × t
Distance problems involving two objects moving in the same direction often involve one object catching up to the other. These problems typically require calculating the distances traveled by each object. When the second object catches up to the first object, both of their distances will be equal. This can be used to set up an equation.
Things to watch out for:
Make sure that you change the units when necessary. For example, if the rate is given in miles
per hour and the time is given in minutes then change the units appropriately.
It would be helpful to use a distance, rate, and time (DRT) table to organize the information for distance problems. Fill up the DRT table with the information given in the problem and set up the equations.
The following diagrams give the steps to solve Distance-Rate-Time Problems. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions.
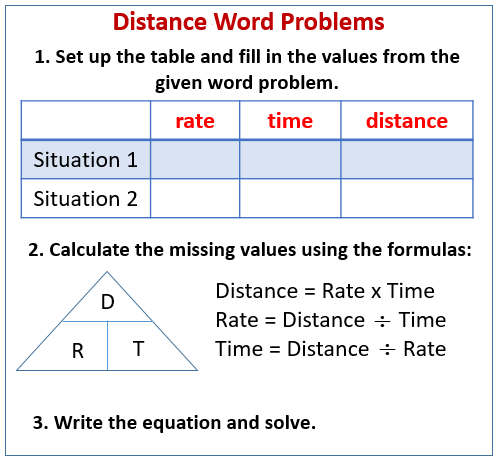
The following diagram gives the steps to solve a Distance-Rate-Time Problem involving two objects going in the same direction and one object catching up to the other.

Key Idea for “Catching up or Overtaking” Problems:
- Distance: If they start from the same point then the distance traveled by both objects are equal when they meet.
- Head Start: Take into consideration the time if any object has a head start.
Types of Distance Word Problems:
Travel in Same Direction
Travel in Opposite Directions
Round Trip Problems
Average Speed Problems
Wind/Current Problems
Printable & Online Algebra Worksheets
Distance Problems: Traveling in the same direction
Example:
A cyclist leaves a town traveling at 15 km/h. Thirty minutes later, another cyclist leaves the same town traveling at 25 km/h in the same direction. How long will it take for the second cyclist to catch up to the first cyclist?
Solution:
Step 1: Set up a rtd table.
| r | t | d | |
| Cyclist 1 | |||
| Cyclist 2 |
Step 2: Fill in the table with information given in the question.
A cyclist leaves a town traveling at 15 km/h. Thirty minutes later, another cyclist leaves the same town traveling at 25 km/h in the same direction. How long will it take for the second cyclist to catch up to the first cyclist?
Let t = time taken for the second cyclist to catch up (in hours). The time taken for the first car would be t + 0.5 since it has a 0.5 hour (30 min) head start.
| r | t | d | |
| Cyclist 1 | 15 | t + 0.5 | |
| Cyclist 2 | 25 | t |
Step 3: Fill in the values for d using the formula d = rt
| r | t | d | |
| Cyclist 1 | 15 | t + 0.5 | 15(t + 0.5) |
| Cyclist 2 | 25 | t | 25t |
Step 4: Since the distances traveled in both cases are the same, we get the equation:
25t = 15(t + 0.5)
Step 5:Solve for t:
25t = 15t + 7.5
10t = 7.5
t = 0.75 hours = 45 minutes
Answer:The second cyclist will catch up to the first cyclist after 45 minutes.
How to solve different types of distance, rate, time problems?
The following examples illustrate three types of problems involving distance, rate and time: opposite directions, same direction and roundtrip.
Example 1:
Lea left home and drove toward the ferry office at an average speed of 22 km.h. Trevon left at the same time and drove in the opposite direction with an average speed of 43 km/h. How long does Trevon need to drive before they are 65 km apart?
Example 2:
Maria left home and traveled toward the capital at an average speed of 80 km/h. Some time later, Imani left traveling in the opposite direction with an average speed of 45 km/h. After Maria has traveled for six hours they were 705 km apart. Find the number of hours Imani traveled.
Example 3:
A passenger train traveled to the repair yards and back. On the trip there, it traveled 68 mph and on the return trip it went 85 mph. How long did the trip there take if the return trip took four hours?
Example 4:
A submarine traveled to St. Vincent and back. It took three hours less time to get there than it did to get back. The average speed on the trip there was 30 km/h. The average speed on the way back was 20 km/h. How many hours did the trip there take?
Example 5:
Micaela left the hardware store and traveled toward her friend’s house at an average speed of 25 km/h. Nicole left some time later traveling in the same direction at the average speed of 30 km/h. After traveling for five hours Nicole caught up with Micaela. How long did Micaela travel before Nicole caught up?
Example 6:
A passenger plane left New York and flew east. A jet left one hour later flying at 280 km/h in a effort to catch up to the passenger plane. After flying for seven hours the jet finally caught up. Find the passenger plane’s average speed.
Check out many other Algebra Word Problems
Age Word Problems, Average Word Problems, Coin Word Problems, Consecutive Integer Word Problems, Digit Word Problems, Distance Word Problems, Fraction Word Problems, Geometry Word Problems, Integer Word Problems, Interest Word Problems, Lever Word Problems, Mixture Word Problems, Money Word Problems, Motion & Distance Word Problems, Number Sequence Word Problems, Proportion Word Problems, Quadratic Equation Word Problems, Ratio Word Problems, Symbol Word Problems, Variation Word Problems, Work Word Problems.
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.