Distributive Property
Related Pages
Math Worksheets
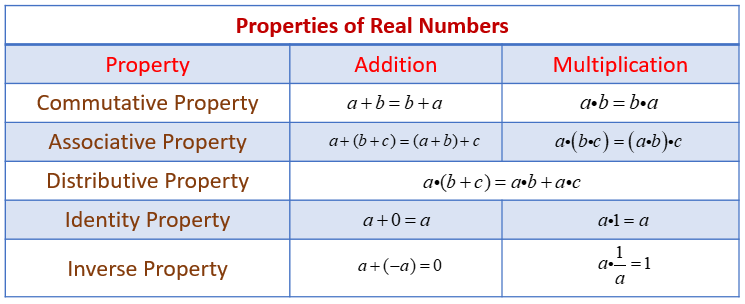
The basic Number Properties (or laws) that apply to arithmetic operations are Commutative Property, Associative Property, Identity Property and Distributive Property.
Number properties are fundamental rules and characteristics that govern how numbers behave under various mathematical operations. Understanding these properties is crucial for simplifying expressions, solving equations, and building a strong foundation in mathematics.
Summary of Number Properties
The following table summarizes the number properties for addition and multiplication: Commutative, Associative, Distributive, Identity and Inverse. Scroll down the page for examples, explanations and solutions.
Worksheets
Practice your skills with the following worksheets:
Printable & Online Numbers Worksheets
Printable & Online Algebra Worksheets
Basic Properties of Addition and Multiplication:
Commutative Property: The order in which numbers are added or multiplied does not change the result.
Addition: a+b=b+a (e.g., 3+5=5+3)
Multiplication: a×b=b×a (e.g., 2×7=7×2)
Check out this lesson on Commutative Property
Associative Property: The way numbers are grouped when adding or multiplying does not change the result.
Addition: (a+b)+c=a+(b+c) (e.g., (1+2)+3=1+(2+3))
Multiplication: (a×b)×c=a×(b×c) (e.g., (4×5)×6=4×(5×6))
Check out this lesson on Associative Property
Identity Property:
Addition: There exists an additive identity, 0, such that a+0=a (e.g., 9+0=9).
Multiplication: There exists a multiplicative identity, 1, such that a×1=a (e.g., 6×1=6).
Check out this lesson on Identity Property
Inverse Property:
Addition: For every number a, there exists an additive inverse (opposite), −a, such that a+(−a)=0 (e.g., 8+(−8)=0).
Multiplication: For every non-zero number a, there exists a multiplicative inverse (reciprocal),
\( \frac{1}{a} \), such that \( a \times \frac{1}{a} \) = 1 (e.g., 3 × \( \frac{1}{3} \) = 1
Distributive Property: Multiplication distributes over addition and subtraction. Distributive property allows you to remove the parenthesis (or brackets) in an expression. Multiply the value outside the brackets with each of the terms in the brackets.
a×(b+c)=(a×b)+(a×c) (e.g., 2×(3+4)=(2×3)+(2×4))
a×(b−c)=(a×b)−(a×c) (e.g., 5×(7−2)=(5×7)−(5×2))
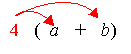
| For example: | 4(a + b) = 4a + 4b |
| 7(2c – 3d + 5) = 14c – 21d + 35 |
What happens if you need to multiply (a – 3)(b + 4)?
You do the same thing but with one value at a time.
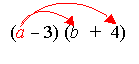
For example:
Multiply a with each term to get a × b + 4 × a = ab + 4a
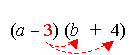
Then, multiply 3 with each term to get “ –3b – 12” (take note of the sign operations).
Put the two results together to get “ab + 4a – 3b – 12”
Therefore, (a – 3)(b + 4) = ab + 4a – 3b – 12
The following video shows more examples of the distributive property.
The following video will discuss the number properties for Algebra.
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.