Electrical Energy Calculations
A series of free GCSE/IGCSE Physics Notes and Lessons.
Electrical Energy and Power
The following diagram gives the formula for Electrical Energy and Power. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions on how to use the formula.
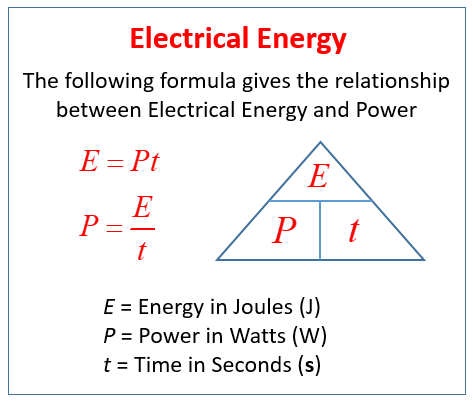
The formula E = Pt is used to calculate electrical energy, where:
E is the electrical energy (in joules, J),
P is the power (in watts, W),
t is the time (in seconds, s).
This formula is derived from the relationship between power, energy, and time.
Explanation:
This formula states that the amount of electrical energy used or consumed is equal to the power of the electrical device multiplied by the time it’s used.
Essentially, power tells you how quickly energy is being used. When you multiply power by time, you get the total amount of energy used.
This formula can be used to determine how much energy an electrical appliance uses over a specific period.
Units:
If power (P) is in watts (W) and time (t) is in seconds (s), then energy (E) will be in joules (J).
If power (P) is in kilowatts (kW) and time (t) is in hours (h), then energy (E) will be in kilowatt-hours (kWh).
kWh are what your home electric bill is measured in.
Electric Power and The Cost of Electricity Using kWh
This physics video explains how to calculate the cost of electricity using electric energy in kWh and by calculating the electric power used by a refrigerator given the voltage and the electric current.
Energy Transfer by Appliances
- Describe how different domestic appliances transfer energy.
- Describe what is meant by the power rating of an appliance.
How appliances transfer electrical energy into other forms such as thermal energy or kinetic energy?
What is meant by the power rating for an appliance?
Calculating energy transferred by appliances
Example:
- A kettle has a power rating of 2200 watts and is used for 80 seconds. Calculate the total energy transferred.
- A fan has a power rating of 20 watts and is used for 1 hour. Calculate the total energy transferred.
- An iron is used for five minutes and a total of 600,000 joules of energy is transferred. Calculate the power of the iron.
- A blender has a power of 400 watts and a total of 48,000 joules of energy is transferred when the blender is in use. Calculate the time that the blender is used for.
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.