Chemistry Required Practical: Electrolysis
Related Topics:
GCSE/IGCSE Chemistry
Chemistry Required Practicals
GCSE/IGCSE Physics
GCSE/IGCSE Biology
GCSE/IGCSE Maths
GCSE Chemistry Required Practical - Electrolysis
Investigate what happens when two different aqueous solutions are electrolysed using inert electrodes.
In this practical you will:
- use a low voltage power supply and carbon rod electrodes to pass a current through two different salt solutions
- identify the element formed at the positive and negative electrodes for each solution
- add extra detail to the basic electrochemical diagram provided.
Method:
- Pour approximately 50 cm3 copper (II) chloride solution into the beaker.
- Add the petri dish lid and insert the carbon rods through the holes. The rods must not touch each other.
- Attach crocodile leads to the rods. Connect the rods to the dc (red and black) terminals of a low voltage power supply.
- Select 4 V on the power supply and switch on.
- Look at both electrodes and record your initial observations in the table below.
- Use forceps to hold a piece of blue litmus paper in the solution next to the anode (positive electrode) and identify the element? Write all your observations in a table.
- Rinse the electrochemical cell apparatus and collect a new set of electrodes.
Repeat steps 1‒8 using the other solution sodium chloride and complete the following tasks to
show your understanding of the chemistry of electrolysis.
a. Draw a fully labelled diagram of your electrochemical cell.
b. What is the third main product of this electrolysis reaction that could be detected with the use of red litmus?
Electrolysis - GCSE Science Required Practical
How to carry out a simple electrolysis of copper chloride and sodium sulphate and write half-equations.
Copper Chloride:
At the Anode:
2Cl- -> Cl2 (g) + 2e-
At the Cathode:
Cu2+ + 2e- -> Cu(s)
Sodium Sulphate:
At the Anode:
4OH- -> O2 (g) + 4e-
+ 2H2O (l)
At the Cathode:
2H+ + 2e- -> H2(g)
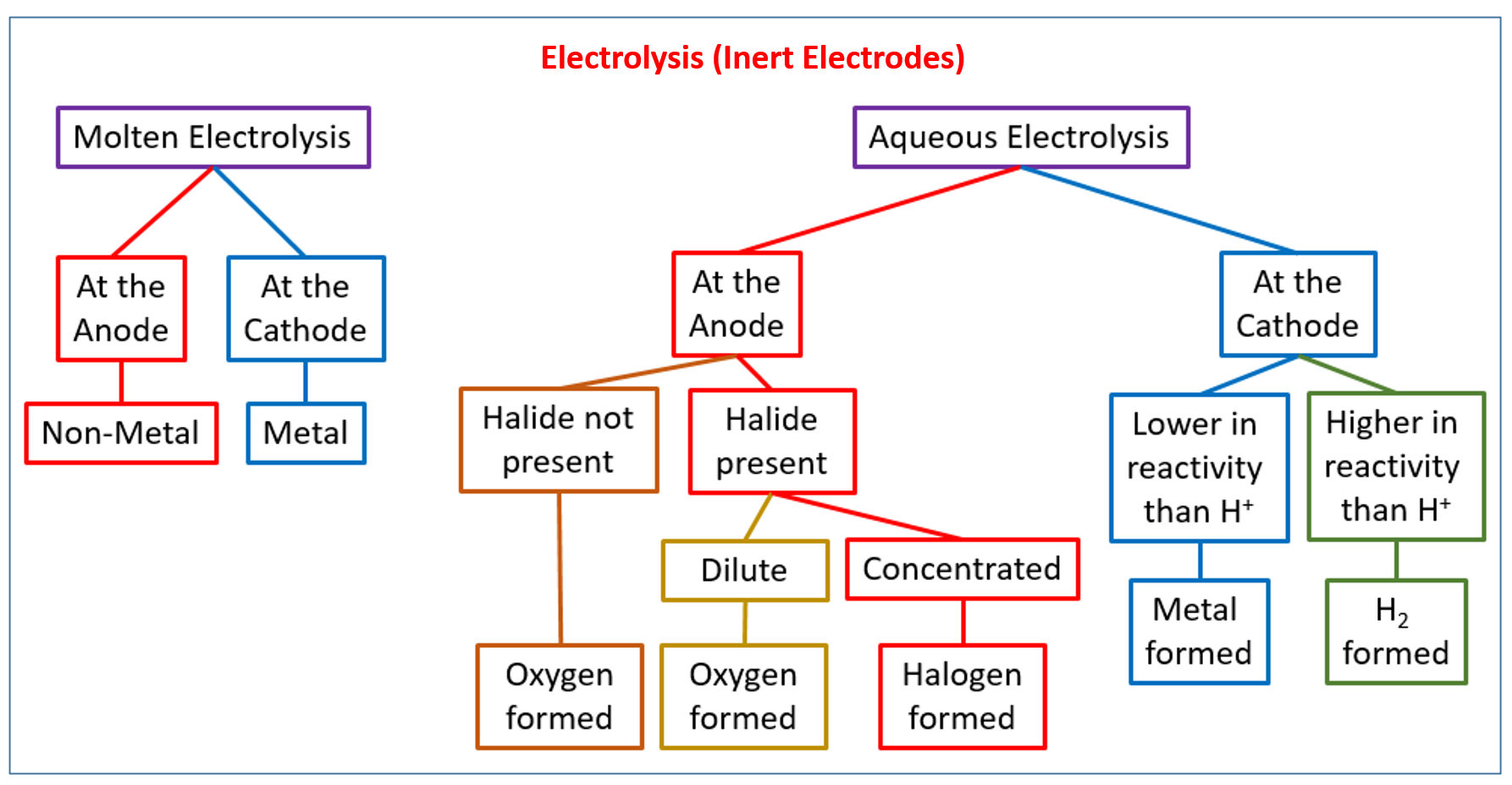
The following diagram gives a flowchart for the electrolysis of molten and aqueous compounds with inert electrodes. This flowchart is useful to determine what products will be formed at the cathode and anode for different electrolytes. Scroll down the page for examples and solutions.
GCSE Science Chemistry Required Practical: Electrolysis
Describe how to investigate what happens when aqueous solutions undergo electrolysis. Copper Chloride and Sodium Chloride.
Copper Chloride:
At the Anode:
2Cl- -> Cl2 (g) + 2e-
At the Cathode:
Cu2+ + 2e- -> Cu(s)
Sodium Chloride:
At the Anode:
2Cl- -> Cl2 (g) + 2e-
At the Cathode:
2H+ + 2e- -> H2(g)
Try the free Mathway calculator and
problem solver below to practice various math topics. Try the given examples, or type in your own
problem and check your answer with the step-by-step explanations.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.