Illustrative Mathematics Grade 7, Unit 7, Lesson 4: Solving for Unknown Angles
Learning Targets:
- I can reason through multiple steps to find unknown angle measures.
- I can recognize when an equation represents a relationship between angle measures.
Related Pages
Illustrative Math
Grade 7
Lesson 4: Solving for Unknown Angles
Let’s figure out some missing angles.
Illustrative Math Unit 7.7, Lesson 4 (printable worksheets)
Lesson 4 Summary
The following diagrams explain how to find unknown angle measures using equations to represent relationships between angle measures.
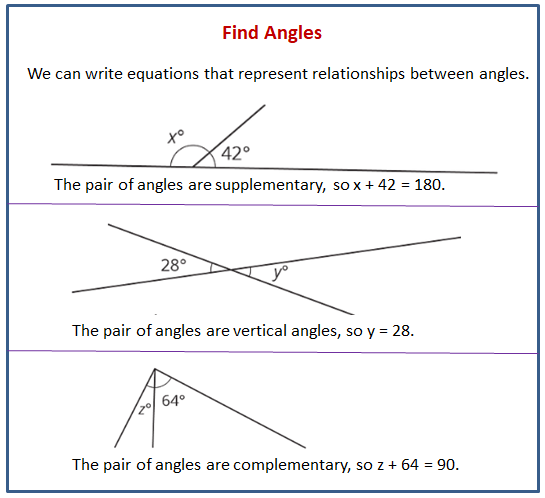
Lesson 4.1 True or False: Length Relationships
Here are some line segments.
Decide if each of these equations is true or false. Be prepared to explain your reasoning.
CD + BC = BD
AB + BD = CD + AD
AC - AB = AB
BD - CD = AC - AB
Lesson 4.2 Info Gap: Angle Finding
Your teacher will give you either a problem card or a data card. Do not show or read your card to your partner.
If your teacher gives you the problem card:
- Silently read your card and think about what information you need to answer the question.
- Ask your partner for the specific information that you need.
- Explain to your partner how you are using the information to solve the problem.
- Solve the problem and explain your reasoning to your partner.
If your teacher gives you the data card:
- Silently read the information on your card.
- Ask your partner “What specific information do you need?” and wait for your partner to ask for information. Only give information that is on your card. (Do not figure out anything for your partner!)
- Before telling your partner the information, ask “Why do you need that information?”
- After your partner solves the problem, ask them to explain their reasoning and listen to their explanation.
Pause here so your teacher can review your work. Ask your teacher for a new set of cards and repeat the activity, trading roles with your partner.
Lesson 4.3 What’s the Match?
Match each figure to an equation that represents what is seen in the figure. For each match, explain how you know they are a match.
Are you ready for more?
- What is the angle between the hour and minute hands of a clock at 3:00?
- You might think that the angle between the hour and minute hands at 2:20 is 60 degrees, but it is not! The hour hand has moved beyond the 2. Calculate the angle between the clock hands at 2:20.
- Find a time where the hour and minute hand are 40 degrees apart. (Assume that the time has a whole number of minutes.) Is there just one answer?
Lesson 4 Practice Problems
- M is a point on line segment KL. NM is a line segment. Select all the equations that represent the relationship between the measures of the angles in the figure.
- Which equation represents the relationship between the angles in the figure?
- Segments AB, EF, and CD intersect at point C, and angle ACD is a right angle. Find the value of g.
- Select all the expressions that are the result of decreasing x by 80%.
- Andre is solving the equation 4(x + 3/2) = 7. He says, “I can subtract 3/2 from each side to get 4x = 11/2 and then divide by 4 to get x = 11/8.” Kiran says, “I think you made a mistake.”
a. How can Kiran know for sure that Andre’s solution is incorrect?
b. Describe Andre’s error and explain how to correct his work. - Solve each equation.
- A train travels at a constant speed for a long distance. Write the two constants of proportionality for the relationship between distance traveled and elapsed time. Explain what each of them means.
The Open Up Resources math curriculum is free to download from the Open Up Resources website and is also available from Illustrative Mathematics.
Try the free Mathway calculator and
problem solver below to practice various math topics. Try the given examples, or type in your own
problem and check your answer with the step-by-step explanations.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.