Forces and Elasticity
A series of free GCSE/IGCSE Physics Notes and Lessons.
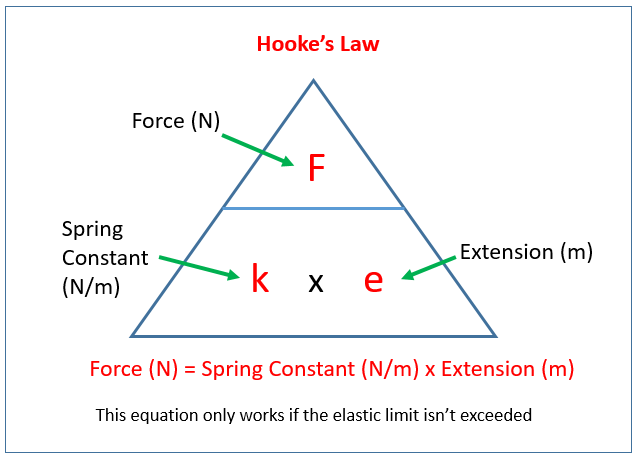
The following diagram gives the formula for Hooke’s Law: force, spring constant, extension.
Forces and Elasticity
State the difference between elastic and inelastic deformations.
Calculate the force needed to stretch or compress an object.
Describe the energy transfers taking place when an elastic object undergoes stretching, compression or bending.
Example:
Calculate the force required to extend a spring by 0.04 metres. The spring constant is 200N/m.
Forces and Elasticity
Elasticity is a measure of an objects ability to resume its original shape after being stretched or compressed.
Try the free Mathway calculator and
problem solver below to practice various math topics. Try the given examples, or type in your own
problem and check your answer with the step-by-step explanations.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.