GRE Quantitative - Fractions
This lesson is part of a series of lessons for the quantitative reasoning section of the GRE revised General Test.
In this lesson, we will learn about
- Equivalent Fractions
- Reducing Fractions
- Mixed Numbers
- Adding and Subtracting Fractions
- Multiplying and Dividing Fractions
Fractions
A fraction is a number of the form, ![]() where x and y are integers. The integer x is called the numerator of the fraction, and y is called the denominator. For example,
where x and y are integers. The integer x is called the numerator of the fraction, and y is called the denominator. For example,
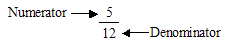
is a fraction in which 5 is the numerator and 12 is the denominator. Such numbers are also called rational numbers.
A fraction with a negative sign in either the numerator or denominator can be written with the negative sign in front of the fraction; for example,
Equivalent Fractions
If both the numerator x and denominator y are multiplied by the same nonzero integer, the resulting fraction will be equivalent to ![]() . For example,
. For example,
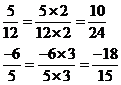
The following video explains: Meaning of Fractions, Equivalent Fractions, Fractions with 0 in numerator or denominator, fractions with 1 in the denominator.
Reducing Fractions
If both the numerator and denominator have a common factor, then the numerator and denominator can be factored and reduced to an equivalent fraction. For example,
The following video shows how to simplify and reduce fractions to lowest terms.
Mixed Numbers
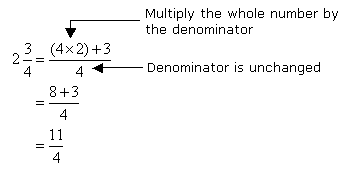
An expression such as ![]() is called a mixed number. It consists of an integer part and a fraction part; the mixed number
is called a mixed number. It consists of an integer part and a fraction part; the mixed number ![]() means 2 +
means 2 +![]()
When converting mixed numbers to improper fractions, we multiply the whole number by the denominator and add to the numerator of the fractional part. The denominator is not changed.
This video shows how to convert mixed numbers to improper fractions and improper fractions to mixed numbers.
Adding and Subtracting Fractions
To add two fractions with the same denominator, you add the numerators and keep the same denominator.
For example,
![]()
To add two fractions with different denominators, first find a common denominator, which is a common multiple of the two denominators. Then convert both fractions to equivalent fractions with the same denominator. Finally, add the numerators and keep the common denominator. The same method applies to subtraction of fractions.
The following video shows how to add and subtract fractions
Multiplying and Dividing Fractions
To multiply two fractions, multiply the two numerators and multiply the two denominators. For example,
To divide one fraction by another, first invert the second fraction—that is, find its reciprocal—then multiply the first fraction by the inverted fraction. For example,
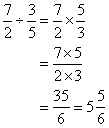
The following video shows how to multiply and divide fractions, including mixed numbers.
Try the free Mathway calculator and
problem solver below to practice various math topics. Try the given examples, or type in your own
problem and check your answer with the step-by-step explanations.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.