Rotation in Geometry
Related Topics:
More lessons on Rotation & other forms of Transformation
Transformation Games & Activities
Videos, worksheets, stories and songs to help Grade 7 students learn about rotation in geometry.
The following diagram gives some rules of rotation. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions.
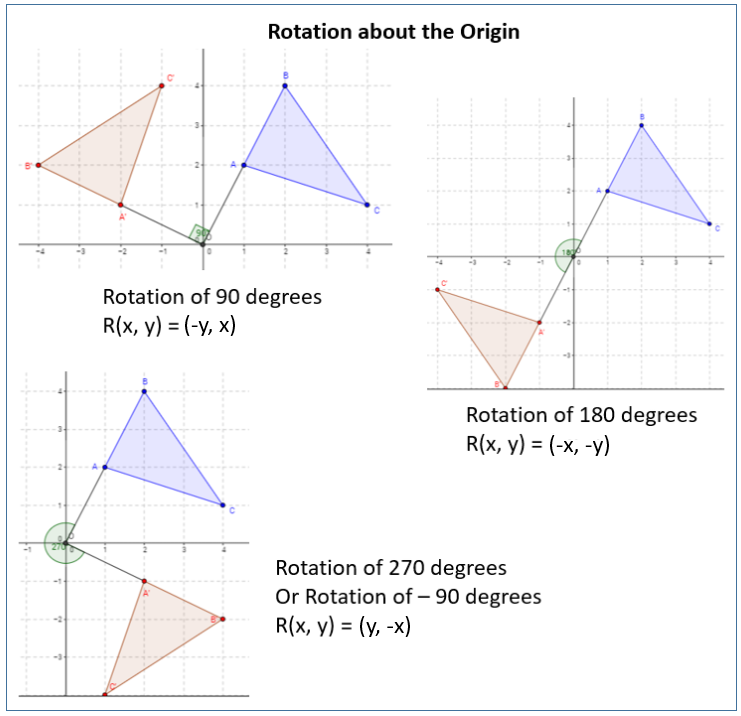
Rotation
A rotation (or turn) is a transformation that turns a line or a shape around a fixed point. This point is called the center of rotation. We usually measure the number of degrees of rotation of a shape in a counterclockwise direction.
Introduction to Rotation
Rotate 90 degrees clockwise
Rotate 90 degrees counterclockwise
Rotate 180 degrees
Math Rotations
Students learn that when a figure is turned to a new position, the transformation is called a rotation.
Estimate the number of degrees and state the direction in which the following figure has been rotated.
Rotation of figures
A video showing how to rotate a figure “x” degrees around a point.
How to rotate a figure 90 degrees rotation about a point O using a compass and a protractor.
Geometry Construction: Rotating a Figure by Hand
How to rotate a figure around a fixed point using a compass and protractor.
Rotate “H” 100 degrees counterclockwise around a point P.
Rotations on the Coordinate Plane
Transformations - Rotate 90 degrees
Rotating a polygon clockwise 90 degrees around the origin.
Step 1: For a 90 degree rotation around the origin, switch the x, y values of each ordered pair for the location of the new point.
Step 2: After you have your new ordered pairs, plot each point.
Rotate 180 Degrees Around The Origin
This tutorial shows why all signs of an ordered pair of an object become opposite when rotating that object 180 degrees around the origin.
A lesson on transformations, with a focus on rotation and reflection
Rules for reflections and rotations on the coordinate plane
Common Rules of Reflection
- Over x-axis: Keep x, change y i.e. (x,y) → (x,-y)
- Over y-axis: Change x, keep y i.e. (x,y) → (x,-y)
- Through origin: Change x, change y i.e. (x,y) → (-x,-y)
- Over the line y = x: Swap x and y i.e. (x,y) → (y,x)
- Over the line y = -x: Swap x and negate i.e. (x,y) → (-y,-x)
Less Common Reflections
To reflect over any line (or point):
- Plot given figure and given line (or point)
- Make a “path” from figure to line (or point)
- Repeat the same “path” to he image.
Common Rules for Rotation
- Rotation of 90°: (x,y) → (-y,x)
- Rotation of 180°: reflect through origin i.e. (x,y) → (-x,-y)
- Rotation of 270°: (x,y) → (y,-x)
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.