In this lesson, we will learn
- what are halogens?
- physical properties of halogens
- chemical properties of halogens
What are the Halogens?
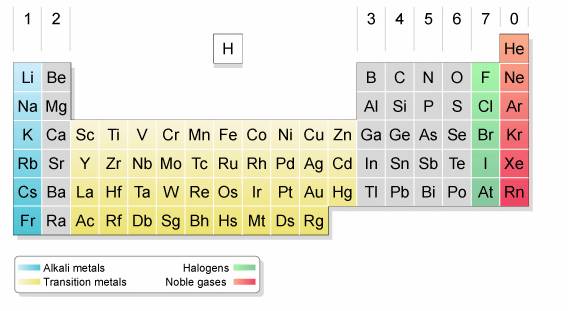
The halogens are the five non-metals in Group 7 of the Periodic Table – fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine and astatine. Astatine is highly radioactive and extremely rare.
The elements in Group 7 are:
Chemical Name |
Chemical Symbol |
Atomic Number |
fluorine |
F |
9 |
chlorine |
Cl |
17 |
bromine |
Br |
35 |
iodine |
I |
53 |
astatine |
At |
85 |
The following diagram shows the halogens and their positions in the periodic table. Scroll down the page for more explanations about the halogens.
Physical Properties of halogens
- Are poisonous
- Brittle and crumbly in their solid form
- Do not conduct electricity
- Form diatomic molecules (containing two atoms). For example Fl2.
- Form colored vapors:
- Fluorine is a pale yellow gas
- Chlorine is a green gas
- Bromine forms a red vapor
- Iodine forms a purple vapor
- Fluorine is a pale yellow gas
Chemical Properties of halogens
- The halogens are among the most reactive elements in the Periodic Table.
- They all have seven valence electrons – seven electrons in their outer-shell.
- They react with metals to form compounds called halides.
Reaction with iron wool
Halogen |
Reaction with iron wool |
The product |
Appearance |
fluorine |
Iron wool bursts into flame as fluorine passes over it – no heating required. |
Iron(III) fluoride, FeF3 |
Pale green solid |
chlorine |
Hot iron wool glows brightly when chlorine passes over it |
Iron(III) chloride. FeCl3 |
Yellow solid |
bromine |
Hot iron wool glows, but less brightly, when bromine vapor passes over it. |
Iron(III) bromide, FeBr3 |
Red-brown solid |
iodine |
Hot iron wool shows a faint red glow when iodine vapor passes over it. |
Iron(III) iodide, FeI3 |
black solid |
Reactivity increases as you go up Group 7
When halogens react with metals, the halogen atoms gain an electron. The smaller the atom the easier it is to attract the electron and the more reactive the element. (This is opposite of the trend in Group 1 where the larger the atom the easier it is to lose an electron.)
Halogens form Ionic and Covalent Compounds
Since halogens have seven electrons in their outer shell, their atoms are only one electron short of a full shell. A halogen atom can gain an electron by accepting an electron from another atom, or sharing an electron with another atom.
Halogens form ionic compounds with metals
When reacting with metals, a halogen atom accepts an electron from the metal atom. The metal atom becomes a positive ion and the halogen atom a negative ion.
Example:
Na + Cl → Na+Cl-
Halogens form covalent compounds with hydrogen and non-metals
When reacting with hydrogen and other non-metals, the halogen atoms share electrons, forming molecules with covalent bonds. Halogens can also form covalent bonds with each other to give diatomic atoms.
Example:
H2 + Cl2 → 2HCl
Physical Properties of the halogens
Chlorine, bromine, iodine
Fluorine
This video shows fluorine reacting with different elements.
Chlorine
The following video shows a reaction between sodium and chlorine. An Erylmeyer flask is filled will chlorine gas by the reaction of hydrochloric acid and potassium permanganate. Sodium metal is placed into the flask and the reaction is catalyzed when a few drops of water is placed on the sodium metal in the flask. What results is an exothermic reaction that produces a white smoke full of NaCl or sodium chloride dust.
Bromine
The following video shows bromine reacting with aluminum. Small lumps of aluminum are added to bromine. The two elements start reacting after a short activation period, forming solid aluminum bromide. The reaction is very exothermic
Iodine
The following video shows how iodine reacts with aluminum powder. After a few minutes, the two start reacting to produce a toxic purple cloud of iodine vapor, aluminum iodide, and a little hydrogen iodide.
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.