I-V Characteristics Experiment: Required Practical
I-V characteristics: GCSE Physics Required Practicals
Investigating the I-V characteristics of circuit components.
- I-V characteristic of a resistor
- I-V characteristic of a filament
- I-V characteristic of a diode
What happens to the current through a component when the potential difference across it changes?
For some circuit components, the value of resistance can change as the current changes. You can use the graph of current against potential difference to help identify the component in a circuit.
In this practical you will:
- construct circuits and draw circuit diagrams
- measure the current across a component as you change the potential difference
- plot graphs of current against potential difference for each component
Activity 1: The characteristic of a resistor
Method
- Set up your circuit with a resistor, ammeter, voltmeter, variable resistor, and suitable power supply.
- Record the readings on the ammeter and voltmeter in a suitable table.
- Adjust the variable resistor and record the new ammeter and voltmeter readings. Repeat this to obtain several pairs of readings.
- Swap the connections on the battery/power supply. Now the ammeter is connected to the negative terminal and variable resistor to the positive terminal. The readings on the ammeter and voltmeter should now be negative.
- Continue to record pairs of readings of current and potential difference with the battery reversed.
- Plot a graph of current against potential difference. As the readings include negative values the origin of your graph will be in the middle of the graph paper.
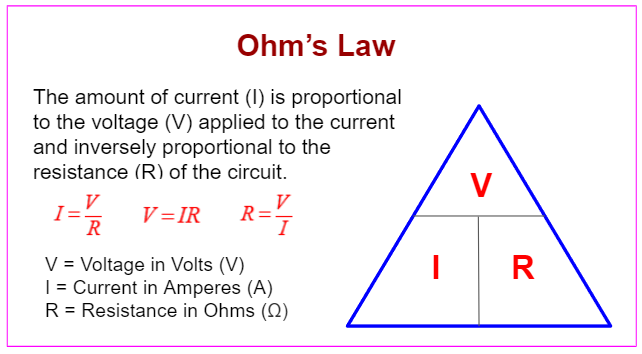
You should be able to draw a straight line of best fit through the origin. This is the I-V characteristic of a resistor would follow the Ohm’s Law.
Activity 2: The characteristic of a filament lamp
Method
- Set up your circuit with a filament lamp, ammeter, voltmeter, variable resistor, and suitable power supply.
- Record the readings on the ammeter and voltmeter in a suitable table.
- Adjust the variable resistor and record the new ammeter and voltmeter readings. Repeat this to obtain several pairs of readings.
- Swap the connections on the battery/power supply. Now the ammeter is connected to the negative terminal and variable resistor to the positive terminal. The readings on the ammeter and voltmeter should now be negative.
- Continue to record pairs of readings of current and potential difference with the battery reversed.
- Plot a graph of current against potential difference. As the readings include negative values the origin of your graph will be in the middle of the graph paper.
You should be able to draw a straight line of best fit through the origin. This is the I-V characteristic of a filament lamp.
Activity 3: The characteristic of a diode
Method
- Set up your circuit with a diode, ammeter, voltmeter, variable resistor, and suitable power supply.
- Record the readings on the ammeter and voltmeter in a suitable table.
- Adjust the variable resistor and record the new ammeter and voltmeter readings. Repeat this to obtain several pairs of readings.
- Swap the connections on the battery/power supply. Now the ammeter is connected to the negative terminal and variable resistor to the positive terminal. The readings on the ammeter and voltmeter should now be negative.
- Continue to record pairs of readings of current and potential difference with the battery reversed.
- Plot a graph of current against potential difference. As the readings include negative values the origin of your graph will be in the middle of the graph paper.
You should be able to draw a straight line of best fit through the origin. This is the I-V characteristic of a diode.
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.