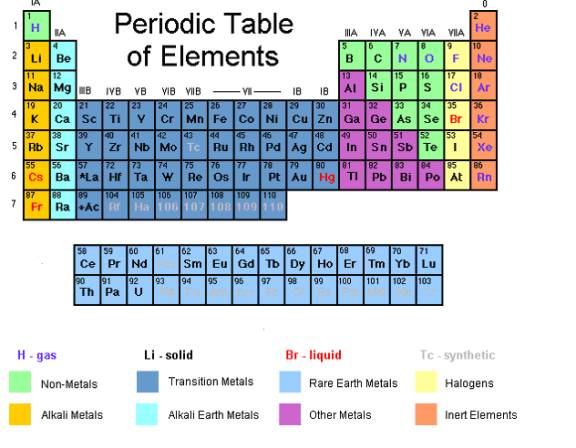
Periodic Table of Elements
Related Topics:
More Lessons for Chemistry
Math Worksheets
What is the Periodic Table?
- The Periodic Table gives the names and symbols of all the elements. It is arranged in order of increasing atomic number (the number of protons).
- The vertical columns are called groups and numbered 0 to 7. Take note that group 0 is at the rightmost column.
- The horizontal rows are called periods. They are also numbered 0 to 7.
Groups in the Periodic Table
The vertical columns of elements on the Periodic Table are called Groups.
Elements in the same group have the same number of electrons in their outer shell (also called the valence electrons). It is the outer electrons of an atom that are mainly responsible for the chemical properties of any element. Therefore, the elements in the same group have similar properties.
Group |
Special name |
Number of valence electrons |
I |
1 |
|
II |
Alkali earth metals |
2 |
III |
- |
3 |
IV |
- |
4 |
V |
- |
5 |
VI |
- |
6 |
VII |
7 |
|
O |
8 (except He) |
Periods in the Periodic Table
The horizontal rows of elements on the Periodic Table are called Periods.
The period numbers give information about the number of electron shells in the atoms. In the elements of Period 2, the atoms have two electron shells. In Period 3 they have three. (But the shell structure gets more complex from Period 4 onwards.)
Metal versus Non-Metal
Over three-quarters of the elements are metals. Only two groups, the halogens and the noble gases, are completely non-metal.
Hydrogen
Hydrogen has one outer electron like the Group 1 metals. However, hydrogen is a gas and usually reacts like a non-metal.
Trends in the Periodic Table
The elements in each numbered group show trends in their properties. For example, as you go down Group 1, the elements become more reactive. As you go down Group 7, they become less reactive.
Videos
Groups of the Periodic TableProperties of alkali, alkaline earth and transition metals, Halogens and noble gases.
The following video looks at 4 main groups of the Periodic Table: Alkali metals, Alkaline Earth metals, Halogens and Noble gases.
Try the free Mathway calculator and
problem solver below to practice various math topics. Try the given examples, or type in your own
problem and check your answer with the step-by-step explanations.



We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.