Permutations And Combinations
Related Pages
Permutations
Counting Methods
Factorial Lessons
Probability
In these lessons, we will learn about permutations and combinations and how to differentiate between them
Combinations and Permutations
Permutations and Combinations are two fundamental concepts in combinatorics, a branch of mathematics dealing with counting. They both involve selecting items from a larger set, but the key difference lies in whether the order of selection matters.
The following table gives some of the differences between permutations and combinations. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions.
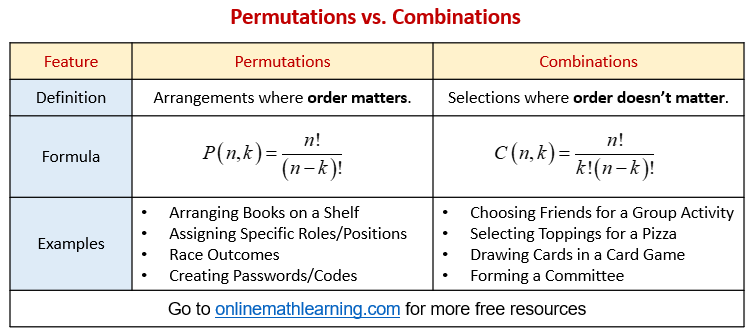
1. Permutations
A permutation is an arrangement of objects where the order of selection matters. Think of it as arranging items in a specific sequence or assigning them to distinct positions.
Key Idea: Order matters. (ABC is different from ACB)
Formulas for Permutations:
Permutations of n distinct items taken k at a time:
This is the number of ways to arrange k items chosen from a set of n distinct items.
The formula is:
\(P\left( n,k \right)=_{n}P_{k}=\frac{n!}{\left( n-k \right)!}\)
Where:
n is the total number of distinct items available.
k is the number of items being chosen and arranged.
! denotes the factorial (e.g., 5!=5×4×3×2×1).
2. Combinations
A combination is a selection of objects where the order of selection does not matter. Think of it as forming a group or a subset where the arrangement of items within the group doesn’t change the group itself.
Key Idea: Order does not matter. (ABC is the same as ACB)
Formulas for Combinations:
Combinations of n distinct items taken k at a time:
This is the number of ways to choose k items from a set of n distinct items, without regard to the order of selection.
The formula is:
\(C\left( n,k \right)=_{n}C_{k}=\frac{n!}{k!\left( n-k \right)!}\)
This formula is derived from the permutation formula by dividing by k! because for every group of k items, there are k! ways to arrange them (which we don’t care about in combinations).
Videos
How to know when to use combinations or permutations?
Both combination and permutation count the ways that (r) objects can be taken from a group of (n) objects, but permutations are arrangements (sequence matters), while combinations are selections (order does not matter).
For example, how many ways can you seat people at a table? That’s permutation. How many poker hands are available in five-card draw? That’s a combination.
Example:
Given a set of seven letters: {a, b, c, d, e, f, g}
How many permutations of three letters?
How many combinations of three letters?
How to find permutations and combinations using factorials?
- I have 20 students in a class. I am going to pick 5 students for a prize. The first person I pick will get 1st prize, the second student 2nd prize and so on. This is called a permutation because the order matters. How many ways can I choose the students?
- I have 20 students in a class. I am going to pick 5 students for a prize. They will all get the same prize. This is called a combination because the order does not matter. How many ways can I choose the students?
Permutations and Combinations
Basic definitions of permutations and combinations.
A permutation is an ordered arrangement of r objects chosen from n objects.
Examples are used to show permutation with repetition and permutation without repetition.
A combination is a selection of r objects chosen from n objects and the order is not important.
Probability - Combinations and Permutations
Fundamental Counting Principle
Example:
- Dana wants to buy a new care. She is trying to choose between a Chevy, Ford, Mazda or a Honda. Each vehicle can come in one of six different colors: black, green, blue, red, silver, or brown. How many different combinations of vehicle and color does Dana have to choose from?
- There are three different color cars parked along the side of the road, a blue car, a red car, and a green car. How many different combinations are there for the order in which these cars are parked?
- Forty-three drivers compete in NASCAR’s Daytona 500 race every year. How many different combinations are there for the first three drivers to cross the finish line?
Permutation with Repetition
Examples:
- How many different ways can the letters in the word FEET be arranged?
- How many different ways can the letters MISSISSIPPI be arranged?
Combinations
Example:
- How many different hands of cards can be dealt from a standard deck of cards?
Multiple Events
Examples:
- Tom and Jen decide to rent a movie. Jen wants to rent a comedy but Tom wants to rent an action movie, so instead they decide to each rent their own movie. The rental kiosk has 16 comedies, 10 action movies, and 14 dramas. How many different combinations of two movies can they rent if they both get the type of movie they want?
- How many different combinations of movies can they rent if they rent at most four movies?
An example using Permutations and Combinations
Examples:
In one game, a code made using different colors is created by one player (the codemaker), and the
player (the codebreaker) tries to guess the code. The codemaker gives hints about whether the colors
are correct and in the right position.
The possible colors are Blue,
Yellow, White, Red, Orange and Green. How many 4-color codes can be made if the colors cannot be repeated?
Examples:
A club of nine people wants to choose a board of three officers: President, Vice President and
Secretary. How many ways are there to choose the board from the nine people?
Example:
A card game using 36 unique cards: four suits (diamonds, hearts, clubs and spades) with cards numbered 1 to 9
in each suit. A hand is a collection of nine cards, which can be sorted however the player chooses. How many
nine card hands are possible?
Example:
To win a particular lottery game, a player chooses 4 numbers from 1 to 60. Each number can only be chosen once.
If all 4 numbers match the winning numbers, regardless of the order, the player wins. What is the probability
that the winning numbers are: 3, 15, 46 and 49?
Quick Ways of Doing Permutations and Combinations.
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.