

Quadrilaterals
More Lessons for GRE Math
Math Worksheets
This lesson is part of a series of lessons for the quantitative reasoning section of the GRE revised General Test. In this lesson, we will learn:
- quadrilaterals; squares, rectangles, parallelograms, trapezoids
- area of quadrilaterals
Quadrilaterals
Every quadrilateral has four sides and four interior angles. The measures of the interior angles add up to 360°.
The following are special quadrilaterals.
• A quadrilateral with four right angles is called a rectangle. Opposite sides of a rectangle are parallel and congruent, and the two diagonals are also congruent.

PQ = SR, PS = QR and PR = QS
• A rectangle with four congruent sides is called a square.
• A quadrilateral in which both pairs of opposite sides are parallel is called a parallelogram. In a
parallelogram, opposite sides are congruent and opposite angles are congruent. Rectangles and squares are also parallelograms.
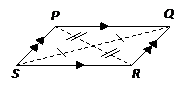
PQ = SR and PS = QR
• A quadrilateral in which two opposite sides are parallel is called a trapezoid.
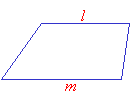 l is parallel to m
l is parallel to m
The following video shows how to classifying quadrilaterals based on the given information.
Area of Quadrilaterals
For all parallelograms, including rectangles and squares, the area A equals the product of the length of a base b and the corresponding height h; that is,
A = bh
Any side can be used as a base. The height corresponding to the base is the perpendicular line segment from any point of a base to the opposite side (or an extension of that side).
Below are examples of finding the areas of a square, a rectangle and a parallelogram.
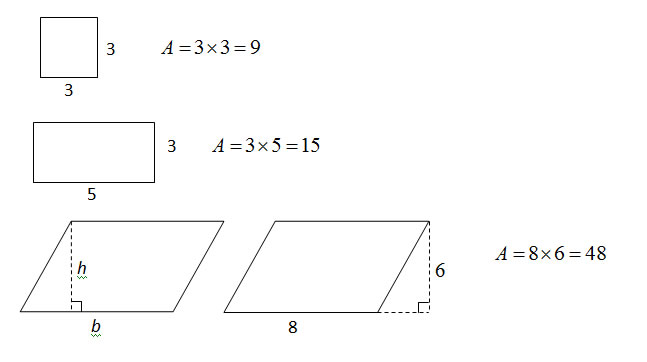
The area A of a trapezoid equals half the product of the sum of the lengths of the two parallel sides a and b and and the corresponding height h; that is,
![]()
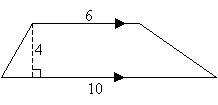
Area of trapezoid
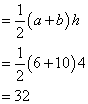
This video gives formulas and examples for how to find the area of squares, rectangles, triangles, parallelograms, and trapezoids. The video also explains the difference between base and height.
Try the free Mathway calculator and
problem solver below to practice various math topics. Try the given examples, or type in your own
problem and check your answer with the step-by-step explanations.



We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.