Scientific Notation
- what is scientific notation
- how to convert from decimal notation to scientific notation
- how to multiply and divide numbers in scientific notation
Scientists have developed 'scientific notation' as a shorter method to express very large and very small numbers.
Scientific Notation is based on powers of the base number 10.
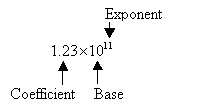
The number 123,000,000,000 in scientific notation is written as:
The first number 1.23 is called the coefficient. It must be greater than or equal to 1 and less than 10. The second number is called the base which must always be 10 in scientific notation. The exponent indicates the power to which 10 must be raised to bring the number to its proper magnitude.
To write a very large number in scientific notation:
1. Move the decimal point to the left until after the first digit. (e.g. 1.23 000 000 000)
2. The number of places moved by the decimal point would be the exponent. (e.g. 11)
3. Then drop the zeroes. (e.g.)
To enter scientific notation in the calculator, use the EXP key.
For example: Enter 1.23 EXP 11 for

A very small number will have a negative exponent, for example:
0.000 000 00712 will be written as 7.12 × 10-9
To write a very small number in scientific notation:
1. Move the decimal point needs to the right until after the first non-zero digit. (e.g. 7.12)
2. The number of places moved by the decimal point would be the negative exponent. (e.g. -9)
The following video shows an example of converting a number in standard notation to a number in scientific notation.
Multiplication of numbers in scientific notation
To multiply numbers in scientific notation:
1. Multiply the coefficients
2. Add the exponentsFor example:
(2.1 × 10-2) × (3.2 × 104)
= 2.1 × 3.2 × 10-2+4
= 6.72 × 102
This video shows how to convert from decimal notation to scientific notation and how to multiply and divide numbers in scientific notation.
Introduction to Scientific Notation and Multiplication in Scientific Notation
Try the free Mathway calculator and
problem solver below to practice various math topics. Try the given examples, or type in your own
problem and check your answer with the step-by-step explanations.



We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.