Secants, Tangents, and Angle Measures
Related Topics:
More Lessons for High School Regents Exam
Math Worksheets
High School Math based on the topics required for the Regents Exam conducted by NYSED.
In circle geometry, secants and tangents are lines that interact with a circle in specific ways, and their intersections (or points of tangency) create angles with unique relationships to the arcs they intercept.
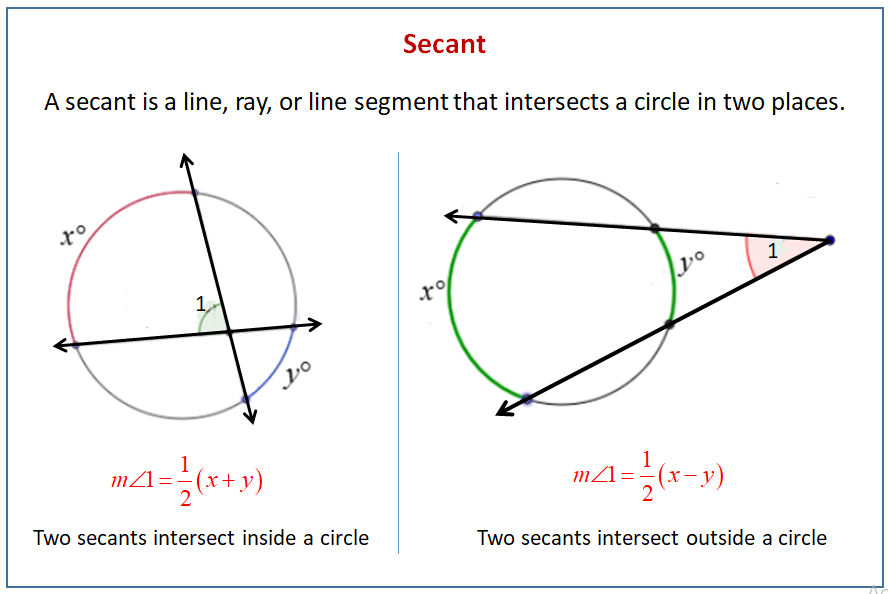
The following diagram gives the formulas for the angles formed when two secants intersect inside a circle and when two secants intersect outside a circle. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions for secants, tangents and angle measures.
Geometry Worksheets
Practice your skills with the following worksheets:
Printable & Online Geometry Worksheets
Definitions
Secant: A line that intersects a circle at two points.
Tangent: A line that touches a circle at exactly one point (the point of tangency).
Chord: A segment whose endpoints lie on the circle.
Angle Measures Formed by Secants and Tangents
A. Tangent-Secant Angle (Vertex Inside the Circle)
Formula:
The angle (θ) formed by a tangent and a secant is half the difference of the intercepted arcs.
\(θ = \frac{1}{2} (\text{major arc + minor arc}) \)
B. Tangent-Secant Angle (Vertex Outside the Circle)
Formula:
The angle (θ) formed by a tangent and a secant is half the difference of the intercepted arcs.
\(θ = \frac{1}{2} (\text{major arc - minor arc}) \)
Secants
Secants, Tangents, and Angle Measures
How to find the measure of an angle if its vertex is inside, outside or on a circle?
Angles in a Circle
This episode deals with angles formed with vertices outside the circle.
Secants
A secant is a line, ray, or line segment that intersects a circle in two places.
Three points are covered:
(1) secants that intersect in a circle which divide each other proportionally,
(2) the angle formed by secants which intersects in a circle and is half the sum of the intercepted arcs
(3) two secants drawn from the same point outside a circle that form an angle whose measure is half the difference of the intercepted arcs.
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.