Tangent Ratio Problems
Related Pages
Trigonometry Word Problems
Lessons On Trigonometry
Trigonometric Identities
In these lessons, we will learn how to find angles and sides using the tangent ratio and how to solve word problems using the tangent ratio. The tangent ratio is a fundamental concept in trigonometry that relates the angles of a right-angled triangle to the lengths of its sides. It’s one of the three primary trigonometric ratios: sine, cosine, and tangent.
Tangent ratio problems involve using the tangent trigonometric function to find missing side lengths or angles in right-angled triangles. The tangent of an angle in a right triangle is defined as the ratio of the length of the side opposite the angle to the length of the side adjacent to the angle.
Definition of the Tangent Ratio:
In a right-angled triangle, for a given acute angle (let’s call it θ), the tangent of that angle (abbreviated as tan θ) is defined as the ratio of:
The length of the side opposite to the angle (Opposite)
The length of the side adjacent to the angle (Adjacent)
Formula:
tan(θ) = Opposite / Adjacent
Understanding the Sides:
Hypotenuse: The longest side of the right-angled triangle, opposite the right angle (90 degrees). The tangent ratio does not involve the hypotenuse.
Opposite Side: The side that is directly across from the angle θ.
Adjacent Side: The side that is next to the angle θ (and is not the hypotenuse).
The following diagram shows the tangent ratio for a right triangle. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions on how to apply the tangent ratio.
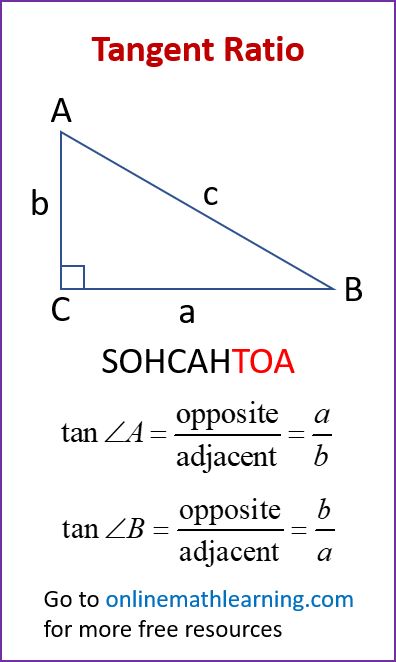
How to Learn and Apply the Tangent Ratio:
- Memorize the Definition: The key is to remember that Tangent = Opposite / Adjacent. A common mnemonic to remember the three basic ratios is SOH CAH TOA:
SOH: Sine = Opposite / Hypotenuse
CAH: Cosine = Adjacent / Hypotenuse
TOA: Tangent = Opposite / Adjacent - Identify the Sides in a Right Triangle: When you’re given a right triangle and a specific angle, make sure you can correctly identify the opposite and adjacent sides relative to that angle.
- Set up the Equation: Once you know the definition and can identify the sides, you can set up an equation to solve for a missing side or a missing angle.
a) Finding a Missing Side: If you know one angle and one side length (either opposite or adjacent), you can use the tangent ratio to find the other side length.
Example: If tan(30°) = Opposite / 10, you can solve for the Opposite side.
b) Finding a Missing Angle: If you know the lengths of the opposite and adjacent sides, you can use the inverse tangent function (arctan or tan⁻¹) to find the angle.
Example: If tan(θ) = 5 / 7, then θ = arctan(5/7).
Trigonometry Worksheets
Practice your skills with the following Trigonometry Worksheets:
Printable & Online Trigonometry Worksheets
How to use the tangent ratio to find missing sides or angles?
Example:
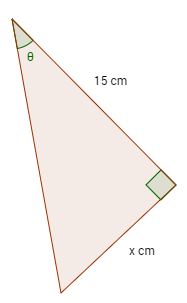
Calculate the length of the side x, given that tan θ = 0.4
Solution:
![]()
Solving Problems with the Tangent Ratio
Examples:
- Find the opposite side given the adjacent side of a right triangle.
- Find the adjacent side given the opposite side of a right triangle.
How to apply the tangent ratio?
A trigonometric ratio is a ratio of the lengths of two sides in a right triangle.
Let triangle ABC be a right triangle with acute angle A. The tangent of angle A is defined as
Tan A = (leg opposite angle A)/(leg adjacent to angle A)
Find missing sides and angle of right triangles.
How to find the opposite side or adjacent side using the tangent ratio?
This video shows you how to use the Tangent Ratio to find the unknown side of a right angle triangle.
What is the tangent ratio and how to use it to find angles and sides in right triangles?
How to use the Tangent Ratio to solve Word Problems?
How to calculate the height of a flag pole using tangent?
The measure of corresponding angles of similar triangle are always equal, so are the ratios of the
corresponding sides.
How to calculate the height of a tree using tangent?
How to use the tangent ratio to find the angle of elevation?
Example:
A toy ladder is set against a 68mm tall stack of coins. If the base of the ladder is 22mm
away from the base of the coins, what angle of elevation does the ladder form?
How to solve Trigonometric Word Problems?
-
From a point on the ground 96 m from a tree, the angle to the top of the tree is 38 degrees. What is the height of the tree?
-
The angle form the ground to the top of the Statue of Liberty is 7 degrees at a distance of 1220 ft from the building. Find the height of the statue.
-
A ladder is leaning up against a house. The bottom of the ladder is 3 ft away from the building and the ladder makes an angle of 75 degrees with the ground.
a) How high up the building does the ladder reach?
b) How long is the ladder? -
A surveyor measured BC to be 125 ft. Find the distance AB across the lake.
-
After takeoff, an airplane maintained a flight angle of 8 degrees with the ground. Find the elevation after it covered after it covered a ground distance of 1200 m.
-
For the airplane in problem 5, find the distance it traveled in the air along the flight path while covering the ground distance of 1200 m.
-
A submarine maintains a diving angle of 22. How far has it travelled when it is directly under a point 350 m along the surface from the point where it submerged?
-
A surveyor wants to find the distance between peaks A and B. He finds point C, 288 ft from peak A, so that ACB is a right angle. The measure BAC is 89. Find the distance AB.
-
Sears Tower is 1454 ft tall. Suppose point A is 1000 ft from the base of the tower. What is the tangent of the angle at A formed by the ground and the line of vision to the top of the tower?
-
Diving at a constant angle A, a submarine descends 102 m while travelling 300 m. Find the degree measure of A.
Hints on solving trigonometry problems:
- If no diagram is given, draw one yourself.
- Mark the right angles in the diagram.
- Show the sizes of the other angles and the lengths of any lines that are known
- Mark the angles or sides you have to calculate.
- Consider whether you need to create right triangles by drawing extra lines. For example, divide an isosceles triangle into two congruent right triangles.
- Decide whether you will need Pythagorean theorem, sine, cosine or tangent.
- Check that your answer is reasonable. The hypotenuse is the longest side in a right triangle.
Try the free Mathway calculator and
problem solver below to practice various math topics. Try the given examples, or type in your own
problem and check your answer with the step-by-step explanations.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.