Trig. Equations Examples using CAST Diagrams
Related Pages
Trigonometric Functions
Trigonometric Graphs
Trigonometric Identities
Lessons On Trigonometry
More Lessons for A Level Maths
These lessons, with videos, examples and step-by-step solutions help A Level Maths students learn to solve trigonometric problems using the CAST diagram.
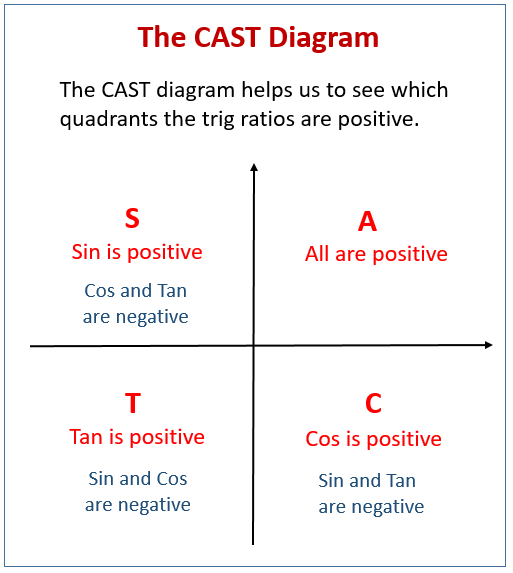
What is the CAST diagram?
The CAST diagram is a useful tool in trigonometry for determining the signs (positive or negative) of trigonometric functions (sine, cosine, and tangent) in different quadrants of the coordinate plane. It helps when solving trigonometric equations.
The Cast diagram helps us to remember the signs of the trigonometric functions in each of the quadrants.
The CAST diagram is also called the Quadrant Rule or the ASTC diagram.
In the first quadrant, the values are all positive.
In the second quadrant, only the values for sin are positive.
In the third quadrant, only the values for tan are positive.
In the fourth quadrant, only the values for cos are positive.
Note that the mnemonic CAST goes anticlockwise starting from the 4th quadrant.
The following diagram shows how the CAST diagram or Quadrant rule can be used. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions.
Trigonometry Worksheets
Practice your skills with the following worksheets:
Printable & Online Trigonometry Worksheets
How to Use the CAST Diagram:
Let’s say you have a trigonometric equation like sin(x) = 0.5, and you want to find all the solutions for x in the range 0° to 360°.
- Find the Principal Value: Use your calculator to find the principal value (the basic solution). sin⁻¹(0.5) = 30°. This is in Quadrant I.
- Use the CAST Diagram to Find Other Solutions:
Since sine is positive in Quadrant I (as we already found) and also in Quadrant II (according to the CAST diagram), there’s another solution in Quadrant II.
To find the solution in Quadrant II, use the formula 180° - principal value. In this case, 180° - 30° = 150°. - List All Solutions in the Given Range: The solutions for sin(x) = 0.5 in the range 0° to 360° are 30° and 150°.
Another Example: cos(x) = -√3/2
- Find the Principal Value: cos⁻¹(-√3/2) = 150°. However, this is not the principal value within the range 0° to 90° that we need for the CAST diagram. Instead, we find the related acute angle using the positive value: cos⁻¹(√3/2) = 30°
- Use the CAST Diagram:
Cosine is negative in Quadrants II and III.
Quadrant II solution: 180° - 30° = 150°
Quadrant III solution: 180° + 30° = 210° - List All Solutions: The solutions for cos(x) = -√3/2 in the range 0° to 360° are 150° and 210°.
Key Points:
- The CAST diagram only tells you where the trigonometric functions are positive. If the value is negative, you look for the quadrants where that function is not listed.
- Always find the principal value (related acute angle) first, usually between 0° and 90°, before using the CAST diagram to find other solutions.
- The angles are measured counterclockwise from the positive x-axis.
Quadrant Rule or CAST diagram
Using the Quadrant Rule to solve trig. equations
Quadrant Rule for solving trig equations with different ranges
Core (2) Graphs of Trigonometric Functions (4) - CAST Diagram or Unit Circle
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.