Set Theory: Union Of Sets
In these lessons, we will learn the union of sets and the complement of the union of sets. For more lessons, see our collection of lessons on sets.
Related Pages
Union Of Sets
Intersection Of Two Sets
Venn Diagrams
More Lessons On Sets
More Lessons for GCSE Maths
Math Worksheets
Union Of Sets
The union of two sets A and B is the set of elements, which are in A or in B or in both. It is denoted by A ∪ B and is read ‘A union B’.
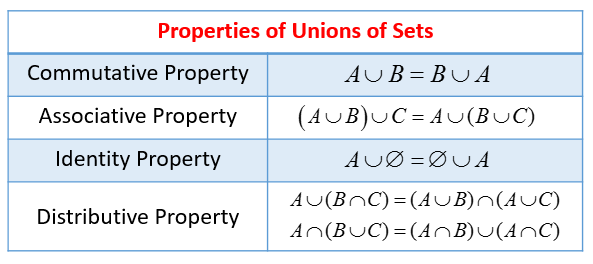
The following table gives some properties of Union of Sets: Commutative, Associative, Identity and Distributive. Scroll down the page for more examples.
Example:
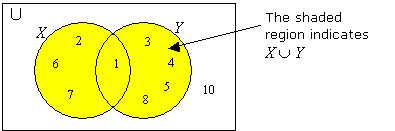
Given U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10}
X = {1, 2, 6, 7} and Y = {1, 3, 4, 5, 8}
Find X ∪ Y and draw a Venn diagram to illustrate X ∪ Y.
Solution:
X ∪ Y = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8} ← 1 is written only once.
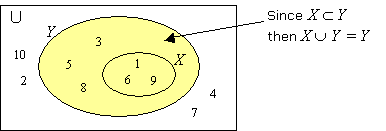
If X ⊂ Y then X ∪ Y = Y.
We will illustrate this relationship in the following example.
Example:
Given U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10}
X = {1, 6, 9} and Y = {1, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9}
Find X ∪ Y and draw a Venn diagram to illustrate X ∪ Y.
Solution:
X ∪ Y = {1, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9}
Complement Of The Union Of Sets
The complement of the set X ∪ Y is the set of elements that are members of the universal set U but are not in X ∪Y. It is denoted by (X ∪ Y)’
Example:
Given: U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}
X = {1, 2, 6, 7} and Y = {1, 3, 4, 5, 8}
a) Draw a Venn diagram to illustrate ( X ∪ Y ) ’
b) Find ( X ∪ Y ) ’
Solution:
a) First, fill in the elements for X ∩ Y = {1}
Fill in the other elements for X and Y and for U
Shade the region outside X ∪ Y to indicate (X ∪ Y)’
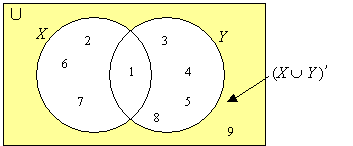
b) We can see from the Venn diagram that
(X ∪ Y)’ = {9}
Or we find that X ∪ Y = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8} and so
(X ∪ Y)’ = {9}
Example:
Given U = {x : 1 ≤ x ≤10, x is an integer}, A = The set of odd numbers, B = The set of factors of
24 and C = {3, 10}.
a) Draw a Venn diagram to show the relationship.
b) Using the Venn diagram or otherwise, find:
i) (A ∪ B ) ’ ii) (A ∪ C ) ’ iii) (A ∪ B ∪ C ) ’
Solution:
A = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}, B = {1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8} and C = {3, 10}
a) First, fill in the elements for A ∩ B ∩C = {3}, A ∩ B {1, 3},
A ∩ C = {3}, B ∩ C = {3} and then the other elements.
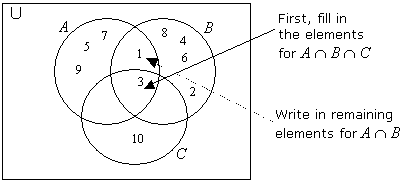
b) We can see from the Venn diagram that
i) (A ∪ B ) ’ = {10}
ii) (A ∪ C ) ’ = {2, 4, 6, 8}
iii) (A ∪ B ∪ C ) ’ = { }
Sets: Union And Intersection
∪ is the union symbol and can be read as “or”. The union of two sets are all the elements form both sets.
∩ is the intersection symbol and can be read as “and”. The intersection of two sets are those elements that belong to both sets.
The intersection of two sets are those elements that belong to both sets.
The union of two sets are all the elements from both sets.
A Mathematics Lesson On Set Operation Of Union
How To Describe The Union And Intersection Of Sets Using Venn Diagrams?
Union, Intersection And Complement
Example:
If D = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10} with subsets A, B and C where A = {4, 6, 8} and B = {6, 7, 8, 9}
and C = {1, 2, 3, 4}, find the following:
A ∩ B
B ∩ C
A ∪ B
B ∪ C
(A ∪ B ∪ C)'
Venn Diagrams: Shading Regions
This video shows how to shade the union, intersection and complement of two sets.
Example:
Shade the indicated region
(1) A ∪ B’
(2) A’ ∩ B’
(3) (A ∪ B)'
Try out our new and fun Fraction Concoction Game.
Add and subtract fractions to make exciting fraction concoctions following a recipe. There are four levels of difficulty: Easy, medium, hard and insane. Practice the basics of fraction addition and subtraction or challenge yourself with the insane level.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.