Vector Quantities
Related Pages
Vectors
Equal Vectors
Common Core (Vector and Matrix Quantities)
Common Core for Mathematics
These lessons, with videos, examples and step-by-step solutions, help High School students recognize vector quantities as having both magnitude and direction. Represent vector quantities by directed line segments, and use appropriate symbols for vectors and their magnitudes (e.g.,v, |v|, ||v||,v).
Common Core: HSN-VM.A.1
The following diagram gives some examples of scalar and vector quantities. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions on how to use scalar and vector quantities.
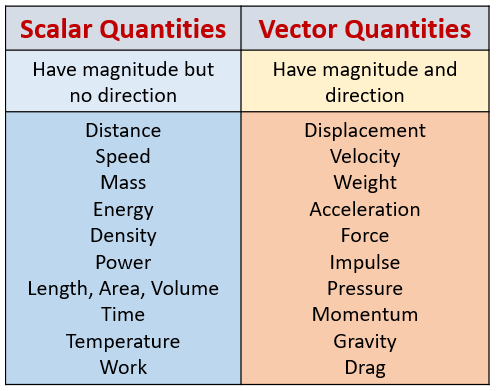
A scalar is a quantity that has only magnitude (size or amount) but no direction. Scalars are described by a single number and a unit.
A vector is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. Vectors are represented graphically as arrows, where the length of the arrow represents the magnitude, and the direction of the arrow represents the direction of the vector.
Vector Basics
An introduction to terminology and how to draw vectors. Two Types of Quantities, Basic Terminology, Vectors, Direction, Draw the Vector 3 m/s at 90°.
Scalars and Vectors
Describes the difference between scalars and vectors.
Scalars and Vectors
This video explains the differences between scalar and vectors quantities. He also uses a demonstration to show the importance of vectors and vector addition.
Vector Quantities
Try the free Mathway calculator and
problem solver below to practice various math topics. Try the given examples, or type in your own
problem and check your answer with the step-by-step explanations.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.